What Is Renewable Energy, Types, Benefits

Renewable energies are flourishing as advancements reduce prices while fulfilling the promise of a clean energy future. American solar and wind generation set records and is seamlessly integrated into the national electricity system.
This means that renewables are gradually replacing “dirty” fossil fuels in the electrical industry, resulting in fewer CO2 emissions and other sorts of pollution. However, not all “renewable” energy sources are environmentally friendly. Here’s everything you need to know about the many sorts of renewable energy sources and how you may use these new technologies in your house.
Table of Contents
What Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy, often known as clean energy, is obtained from renewable resources that are renewed naturally over time. Solar energy, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat are all part of it.
In contrast to fossil fuels, renewable energy is depleted far faster than it is supplied. Although most renewable energy sources are environmentally friendly, some are not. At current utilisation rates, some biomass sources, for example, are considered unsustainable.
Renewable energy sources often supply energy in four important areas: power generation, air, and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services. About 20% of the world’s energy consumption by mankind comes from renewable sources, including approximately 30% of electricity.
About 8% of energy usage is conventional biomass, however this proportion is dropping. More than 4% of the energy consumption is used for thermal energy from current renewable resources, such as solar water heating, and more than 6% for electricity.
Types Of Renewable Energy
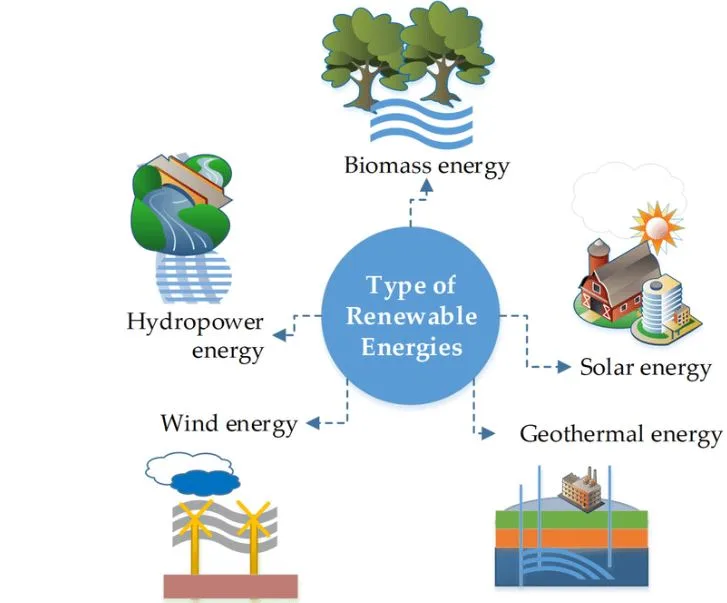
Renewable energy is energy derived from naturally renewing but flow-limited sources; renewable resources are nearly endless in terms of duration but restricted in terms of energy available per unit of time.
The following are the primary types or sources of renewable energy:
- The sun’s solar energy
- Geothermal energy is generated by the heat that exists within the earth.
- Wind power
- Plant-based biomass
- Flowing water hydropower
Renewable energy sources are so named because they are naturally regenerated. Every day, the sun shines, plants grow, the breeze blows, and rivers flow.
1. Solar Energy
Solar power is the conversion of solar energy into thermal or electrical energy. The United States boasts some of the world’s most abundant solar resources, making solar energy the cleanest and most plentiful renewable energy source available.
Solar technology can use this energy to generate electricity, provide light or a warm interior atmosphere, and heat water for domestic, commercial, or industrial use.
Photovoltaics, solar heating and cooling, and concentrating solar power are the three methods for utilising solar energy. Photovoltaics employ an electrical method to create electricity directly from sunshine and can be used to power everything from calculators and traffic signs to homes and huge commercial organisations.
Solar heating and cooling (SHC) and concentrating solar power (CSP) applications both employ solar heat to provide space or water heating in the case of SHC systems, or to power In the case of CSP power plants, typical electricity-generating turbines.
2. Wind Energy
Wind power or wind energy refers to the practise of harnessing the wind to generate mechanical power or electricity. Wind turbines transform wind kinetic energy into mechanical power. This mechanical power can be employed for specialised tasks (such as grain grinding or water pumping) or transformed into energy by a generator.
You can study how wind turbines generate electricity and see an illustration of the components within a wind turbine, or you can watch a wind power animation that shows how moving air turns a wind turbine’s blades and how the internal components work to generate electricity.
3. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is heat extracted from the earth’s crust. It can be found in rocks and fluids beneath the crust as deep as the earth’s boiling molten rock, magma.
Wells are dug a mile underground to obtain steam and hot water, which can subsequently be utilised to power turbines coupled to electricity generators.
The oldest form of geothermal technology, dry steam, extracts steam from the earth and utilises it to directly drive a turbine. Flash plants convert high-pressure hot water to cool, low-pressure water, whereas binary plants convert hot water to vapour by passing it through a second liquid with a lower boiling point.
4. Tidal Energy

The surge of ocean waters during tide rise and fall generates tidal energy. Tidal energy is a renewable energy source.
Engineers discovered methods to harness tidal movement to generate power in regions where there is a considerable tidal range the difference in area between high tide and low tide during the twentieth century. To transform tidal energy into electricity, all techniques need special generators.
Tidal energy production is still in its infancy. So yet, the amount of power produced has been little. There are only a few commercial-scale tidal power facilities in operation around the world.
5. Hydroelectric Power

Hydroelectric energy is a type of energy that generates electricity by harnessing the power of moving water, such as water flowing down a waterfall. It is also known as hydroelectric power or hydroelectricity. For millennia, people have exploited this force.
Over two thousand years ago, people in Greece used flowing water to turn the wheel of their mill, which pounded wheat into flour.
Most hydroelectric power plants contain a water reservoir, a gate or valve that controls how much water comes out of the reservoir, and an outlet or location where the water ends up after flowing downstream. Just before it spills over the top of a dam or runs down a hill, water gains potential energy.
Potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as water flows downhill. Water can be utilised to turn turbine blades, producing electricity that is then distributed to the power plant’s customers.
6. Biomass Energy
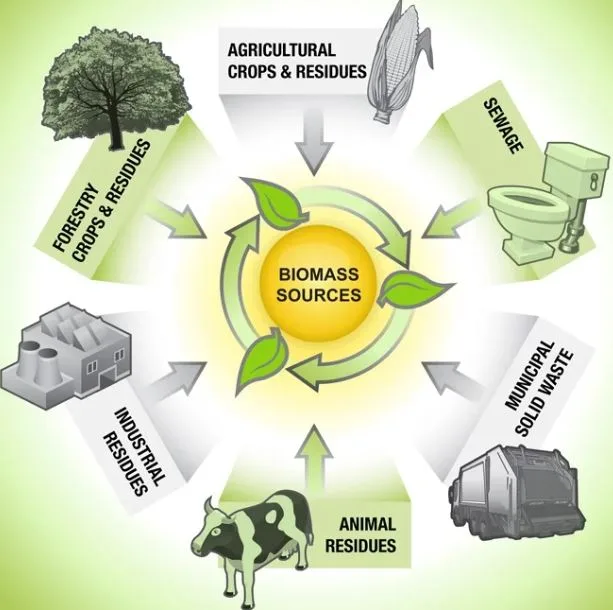
Energy generated or produced by living or once-living creatures is referred to as biomass energy. Plants, such as corn and soy, are the most commonly used biomass feedstock for energy. These organisms’ energy can be burned to generate heat or transformed into electricity.
People have been using biomass energy from living things since the first “cavemen” built wood fires for cooking and heating.
Organic biomass is made up of material derived from living organisms such as plants and animals. Plants, wood, and garbage are the most frequent biomass materials utilised for energy. These are referred to as biomass feedstocks. Biomass energy can also be a nonrenewable source of energy.
Plants absorb the sun’s energy through photosynthesis and transform carbon dioxide and water into nutrients, resulting in biomass (carbohydrates).
Benefits Of Renewable Energy
Environmental and economic advantages of utilizing renewable energy include:
- Creating electricity from fossil fuels that emits no greenhouse gases and lowers some types of air pollution
- Diversifying energy sources and reducing dependency on imported fuels
- Economic growth and employment creation in manufacturing, installation, and other industries
- Renewable energy will never run out.
- Renewable energy requires less upkeep.
- Renewable energy saves money.
- Renewable energy provides various environmental benefits
- Renewable energy sources reduce reliance on foreign energy sources.
- Cleaner water and air are the result of renewable energy.
- Renewable energy generates jobs.
- Renewable energy helps reduce waste.
- Renewable energy has the potential to reduce waste.
Here are some of the most significant advantages of becoming green:
1. Renewable Energy Won’t Run Out
Electricity is generated directly from the environment using renewable energy technologies. Sunlight, wind, tides, and biomass are just a handful of the most prominent energy sources.
Renewable resources are not depleting, although many forms of fossil fuels are. As we use more fossil fuel resources, they become more harder to obtain, raising both the expense and the environmental effect of extraction.
2. Maintenance Requirements Are Lower
Renewable energy systems, in most cases, require less total maintenance than standard fuel-powered generators. This is due to the fact that generation technology such as solar panels and wind turbines have few or no moving components and do not function on flammable, combustible fuel sources. Fewer maintenance required equals more time and money saved.
3. Renewables Save Money
You can save money in the long run by using renewable energies. You save not only on maintenance but also on operating costs. You don’t have to pay to refuel if you use equipment that generates electricity from the sun, wind, steam, or natural processes.
The amount of money saved by using renewable energy depends on a variety of factors, including the technology itself. In most situations, switching to renewable energy results in savings ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
4. Renewable Energy Provides Numerous Health and Environmental Advantages
- Creating electricity from fossil fuels that emits no greenhouse gases and lowers some types of air pollution
- Diversifying energy sources and reducing dependency on imported fuels
- Economic growth and employment creation in manufacturing, installation, and other industries
The use of fossil fuels produces not just greenhouse gases, but also other toxic chemicals that cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. You may assist to minimise the spread of harmful contaminants and contribute to a healthy environment by using renewable energy.
5. Renewables Lower Reliance On Foreign Energy Sources
Renewable energy technologies enable you to generate energy on a small scale. The more renewable energy you utilise for your power needs, the less you rely on imported energy and the greater your contribution to the overall energy independence of the United States.
Disadvantages Of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy offers numerous advantages, but it is not always a pleasant experience. Here are several drawbacks to adopting renewables instead of traditional fuel sources:
- High upfront costs
- Intermittency
- Storage capabilities
- Geographic limitations
- Renewables aren’t always 100% carbon-free
1. Higher Upfront Cost
While adopting renewable energy might save money, the technologies are usually more expensive up front than traditional energy sources. To offset this, financial incentives such as tax credits and rebates are frequently given to help reduce the initial expenses of renewable technologies.
2. Intermittency
Although there are renewable energy sources all around the world, many of them aren’t accessible all the time. Some days may be windier than others, the sun may not shine at night, and droughts may occur for an extended period of time. Unpredictable weather occurrences can affect these technologies. Non-intermittent fossil fuels can be turned on and off at any moment.
3. Storage Capabilities
There is a considerable need for energy storage as a result of the disruption of some renewable energy sources. Although storage technologies are now accessible, they can be costly, particularly for big renewable energy systems. It’s worth mentioning that as technology progresses, energy storage capacity expands and batteries become more affordable.
4. Geographic Limitations
The geography of the United States is diversified, with various climates, topographies, vegetation, and other features. This results in a beautiful melting pot of landscapes, but it also means that some locations are better suited to renewable technologies than others.
A vast open area farm, for example, can be an excellent location for a home wind turbine or solar system, whereas a townhouse in a city covered by higher buildings cannot benefit from either technology on their land. There are other possibilities if your property is not suitable for personal renewable energy technologies.
FAQs.
What Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy, often known as clean energy, is obtained from renewable resources that are renewed naturally over time. Solar energy, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat are all part of it.
What Are The 5 Renewable Energies?
There are five major renewable energy sources:
Solar energy from the sun.
Geothermal energy from heat inside the earth.
Wind energy.
Biomass from plants.
Hydropower from flowing water.
What Exactly Is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is energy derived from naturally renewing but flow-limited sources; renewable resources are nearly endless in terms of duration but restricted in terms of energy available per unit of time. Biomass is the most common sort of renewable energy source. Wood and its byproducts.
What Are Renewable Energy Sources Give Two Examples?
Solar energy, wind, falling water, the heat of the earth (geothermal), plant materials (biomass), waves, ocean currents, temperature differential in the oceans, and tide energy are all renewable resources.