What Is Solar Cell?
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that uses the photovoltaic effect to convert light energy directly into electricity. It is a type of photoelectric cell, which is described as a device with electrical properties that vary when exposed to light, such as current, voltage, or resistance.
Individual solar cell devices are frequently used as electrical components of photovoltaic modules, also known as solar panels in colloquial parlance. The typical single-junction silicon solar cell has an open-circuit voltage of about 0.5 to 0.6 volts.
Solar cells are referred to as photovoltaics regardless of whether they are powered by sunlight or artificial light. They can be used as photodetectors (e.g., infrared detectors) to detect light or other electromagnetic radiation in the visible range, as well as to quantify light intensity.
To work, a photovoltaic (PV) cell must have three basic characteristics:
- Light absorption that produces electron-hole pairs or excitons.
- The separation of oppositely charged charge carriers.
- The removal of these carriers independently to an external circuit.
A solar thermal collector, on the other hand, gathers sunlight and turns it into heat, which may subsequently be utilised to generate electricity. A “photo electrolyte cell,” on the other hand, is either a type of photovoltaic cell or a device that uses solar radiation to split water directly into hydrogen and oxygen.
Photovoltaics and solar panels are used to generate solar energy.
Table of Contents
What Is Solar Cell, Types, Construction & Working
Construction Of Solar Cells
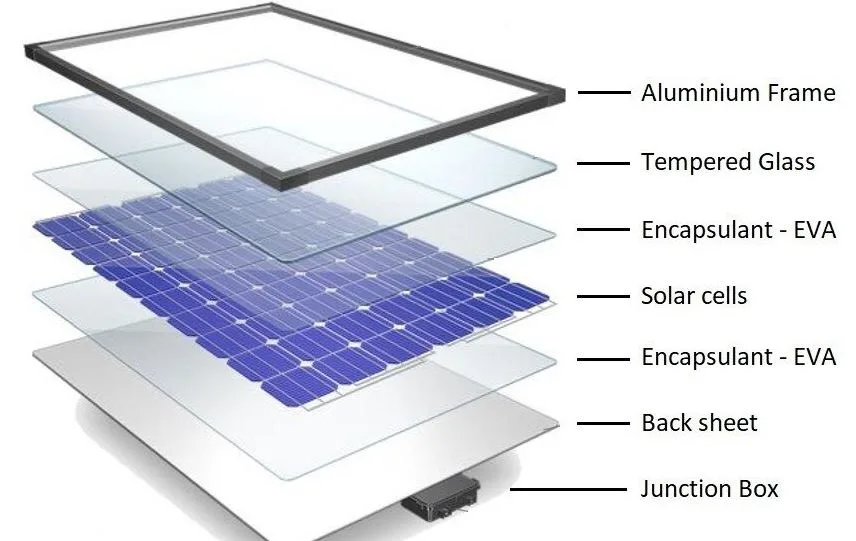
The majority of photovoltaic solar cells, or PV cells, are produced from crystalline silicon wafers. Wafers can be monocrystalline (mono) or polycrystalline (poly), sometimes known as multi-crystalline. The most efficient kind is monocrystalline, which is made using the well-known Czochralski technique.
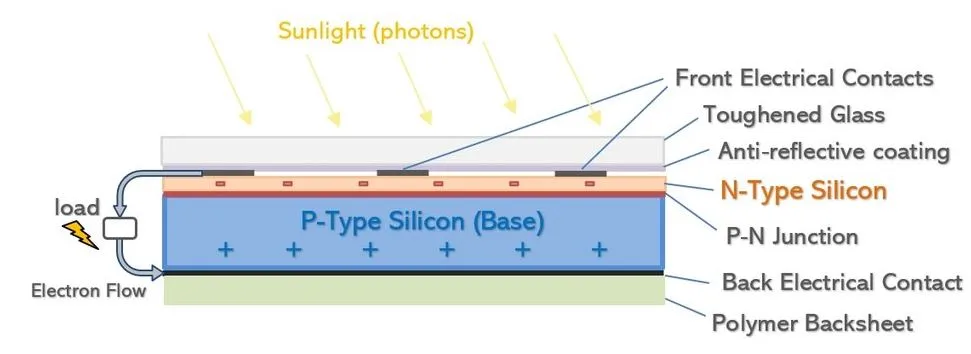
A solar cell is essentially a junction diode, albeit its construction differs slightly from typical p-n junction diodes. A very thin layer of p-type semiconductor is formed on a considerably thicker n-type semiconductor. Then we placed finer electrodes on top of the p-type semiconductor layer.
The thin p-layer is not blocked from receiving light by these electrodes. A p-n junction can be found immediately below the p-layer. We additionally include a current-collecting electrode at the n-base. layer’s To shield the solar cell from mechanical impacts, the whole assembly is encased in thin glass.
Each cell unit produces very little output voltage and current. The current is 0.8V and the output voltage is 0.6V. The varied cell arrangements are utilised to boost output effectiveness.
How Do Solar Cells Work?
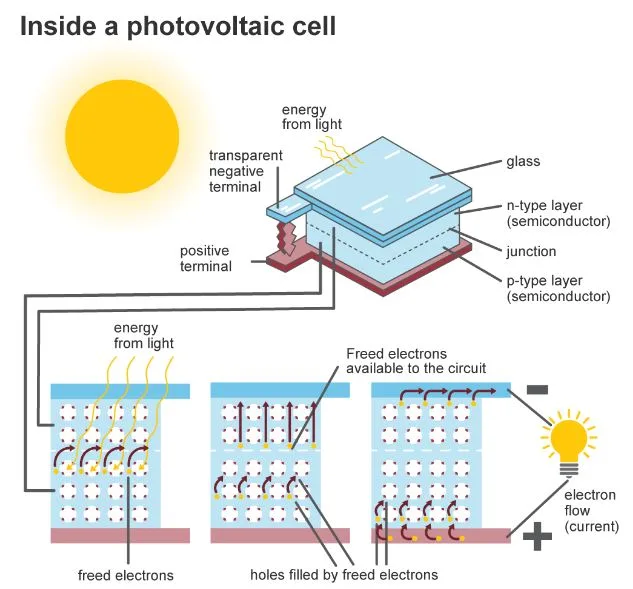
When sunlight strikes a solar cell, electrons are evacuated from the silicon, resulting in “holes” – the voids left by the fleeing electrons. When this occurs in an electric field, the field causes electrons to flow to the n-layer and holes to move to the p-layer.
When the n-type and p-type layers are connected with a metal wire, electrons migrate from the n-type layer to the p-type layer by crossing the depletion zone and then through the external wire back of the n-type layer, resulting in an electric current flow.
A solar cell is made of n-type and p-type silicon sandwiched together. It generates power by bouncing electrons over the link between the various flavours of silicon:
- When sunlight strikes the cell, photons (light particles) bombard the upper surface.
- Photons transport energy down through the cell.
- Photons provide energy to electrons in the lower p-layer.
- This energy is used by the electrons to cross the barrier into the higher, n-conductive layer and escape into the circuit.
- Electrons pass through the circuit and produce electricity.
Types Of Solar Cell

A solar cell is a solid-state electrical device that uses the photovoltaic effect to convert light energy directly into electricity.
It is a type of photoelectric cell, which is described as a device with electrical characteristics that change when exposed to light, such as current, voltage, or resistance.
The various types of solar cells are as follows.
- Amorphous Silicon solar cell (a-Si)
- Biohybrid solar cell
- Cadmium telluride solar cell (CdTe)
- Concentrated PV cell (CVP and HCVP)
- Copper indium gallium selenide solar cells (CI(G)S)
- Crystalline silicon solar cell (c-Si)
- Float-zone silicon
- Dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC)
- Gallium arsenide germanium solar cell (GaAs)
- Hybrid solar cell
- Luminescent solar concentrator cell (LSC)
- Micromorph (tandem-cell using a-Si/μc-Si)
- Monocrystalline solar cell (mono-Si)
- Multi-junction solar cell (MJ)
- Nanocrystal solar cell
- Organic solar cell (OPV)
- Perovskite solar cell
- Photoelectrochemical cell (PEC)
- Plasmonic solar cell
- Polycrystalline solar cell (multi-Si)
- Quantum dot solar cell
- Solid-state solar cell
- Thin-film solar cell (TFSC)
- Wafer solar cell or crystalline wafer-based solar cell
- Non concentrated hetrogeneos PV cell
Monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar modules are the three varieties of solar modules. Each of these types of solar cells is made differently and has a different aesthetic appeal. The following is a breakdown of each type of solar panel.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are the most traditional and advanced type of solar panel. These monocrystalline solar panels are composed of about 40 monocrystalline solar cells. These solar cells are composed entirely of silicon.
During the manufacturing procedure (the Czochralski process), a silicon crystal is immersed in molten silicon. The crystal is then slowly drawn out of the vat, causing the molten silicon to create a solid crystal shell around it known as an ingot. After that, the ingot is thinly sliced into silicon wafers. The wafer is manufactured into cells, which are subsequently combined to produce a solar panel.
Monocrystalline solar cells seem black due to the way sunlight interacts with pure silicon. While the cells are all black, the backs and frames are available in a variety of colours and styles. The monocrystalline cells are square and have had their corners removed, resulting in minor gaps between them.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Despite being a relatively new product, polycrystalline solar panels are quickly becoming more and more popular and effective. Polycrystalline cells, like monocrystalline solar modules, are constructed of silicon. Contrarily, polycrystalline cells are made of fused silicon crystal fragments.
The silicon crystal is placed in a vat of molten silicon during the production process. You let the crystal to crack and cool rather than gradually dragging it out. When the new crystal has completely cooled, it is thinly sliced into polycrystalline solar wafers. An assembly of these wafers results in a polycrystalline panel.
Thin-Film Solar Panels

A remarkably recent innovation in the solar panel market is thin film solar panels. The fact that thin-film panels are not usually constructed of silicon is their key distinguishing characteristic. Cadmium telluride (CdTe), amorphous silicon (a-Si), copper indium gallium selenide, and other substances can be used to make them (CIGS).
The primary material is sandwiched between two thin sheets of conductive material, and a protective covering of glass is placed on top. While silicon is present in the a-Si panels, it is non-crystalline, and the panels are also covered in glass.
Thin-layer panels are easily identified by their thin look, as the name implies. These panels are approximately 350 times thinner than those made with silicon wafers. However, thin-film frames can be rather big, causing the overall look of the solar system to resemble that of a mono- or polycrystalline system. Depending on the substance, thin-film cells might be black or blue.
Material Uses In Solar Cell
Solar cells are often named after the semiconducting substance from which they are constructed. To absorb sunlight, these materials must possess particular properties.
- Crystalline silicon
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si)
- Copper-Indium Gallium Diselenide (CIGS)
- Gallium arsenide thin film
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe)
- Monocrystalline silicon
- Epitaxial silicon development
- Polycrystalline silicon
- Ribbon silicon
- Mono-like-multi silicon (MLM)
Advantages Of Solar Cell
- Renewable energy: Solar power systems (PV or thermal) can be used to heat and power a home.
- Economic Energy: Solar cells are an excellent way to reduce the cost of your electricity bill because you are not charged for the energy you produce.
- Environment-friendly energy Almost no pollutants are released by solar cells. Throughout the solar cell manufacturing process, waste and contamination are inevitable.
- One of the main topics in green energy is photovoltaics, which is regarded as a viable solution to stop climate change.
- You will always have enough energy if you have the ability to draw it from the sun’s rays.
- Lengthy-term energy: The service life of PV systems is typically quite long and good.
- Selling energy: You might be able to get more money when you sell your house if it has solar panels.
Disadvantages Of Solar Cell
- Interior requirements: Not all houses meet their criteria and can get the most out of their solar cells.
- Expensive investment is required: Solar module installation expenses are rather high.
- Seasonal energy: The solar power plant is significantly seasonal when compared to other sources of renewable energy.
- Difficulty installing solar panels in your home: Installing solar panels in older homes may be more difficult because they generally have distinct architecture that can provide shade.
Use Of Solar Cell
- Solar cells are extremely useful for powering spacecraft such as satellites and telescopes.
- It may be used to charge batteries.
- Used in light meters.
- Calculators and wristwatches run on it.
- It can be utilised to provide electrical energy in spacecraft.
FAQs.
What Is Solar Cell?
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that uses the photovoltaic effect to convert light energy directly into electricity. It is a type of photoelectric cell, which is described as a device with electrical characteristics that change when exposed to light, such as current, voltage, or resistance.
What Is The Construction Of A Solar Panel?
A solar cell is essentially a junction diode, albeit its construction differs slightly from that of typical p-n junction diodes. On top of a thicker layer of n-type semiconductor, a thin layer of p-type semiconductor is formed. Then, on top of the p-type semiconductor layer, a few finer electrodes are placed.
How Do Solar Cell Work?
A solar cell is made of n-type and p-type silicon sandwiched together. It creates energy by causing electrons to jump across the junction between the two flavours of silicon using sunlight: Photons (light particles) attack the cell’s upper surface when sunlight shines on it.
What Is Solar Cell And How It Works?
A solar cell is made up of two layers of silicon that have been treated to allow energy to flow between them when exposed to sunshine. The first layer has a positive charge, whereas the second has a negative charge. When photons enter the layers, their energy is transferred to the silicon atoms in the form of electrons.
What Is Called Solar Cell?
When light strikes a photovoltaic (PV) cell, also known as a solar cell, it can be reflected, absorbed, or flow directly through the cell. The PV cell is made of semiconductor material, which conducts electricity better than an insulator but not as well as a good conductor like metal.
What Is The Structure Of Solar Cell?
A solar cell is made up of a layer of p-type silicon sandwiched between two layers of n-type silicon. There is an overabundance of electrons in the n-type layer, and an excess of positively charged holes in the p-type layer (which are vacancies due to the lack of valence electrons).
Where Are Solar Cells Used?
Solar cells have traditionally been utilised in situations when grid power is unavailable, such as distant area power systems, Earth-orbiting satellites, consumer systems, such as handheld calculators or wristwatches, remote radio-telephones, and water pumping applications.
What Is Solar Cell Class 10?
A solar cell is a device that directly transforms solar energy (or the energy of the sun) into electricity. A solar cell turns the energy of the sun into electrical energy. Solar cells are typically constructed of silicon.
What Is The Symbol Of Solar Cell?
The symbol is depicted below. As seen in the diagram, a solar cell is similar to a diode. It is built of silicon, germanium PN junction with a glass window on the top surface layer of P-Type, the P-Type material is thin and wide so that incident light photons can readily reach the PN junction.