What Is Solar Panel?
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types. Solar panels use sun energy to produce electricity.
Solar cells make up a solar panel. A vast number of tiny solar cells dispersed across a big area can work together to provide enough electricity to be useful. A cell generates more electricity the more light it absorbs.
A photovoltaic (PV), solar electric, or plain old solar panel are other names for a solar cell panel. A PV panel is a collection of PV modules, whereas an array is a PV panel system. Photovoltaic arrays provide solar electricity to electrical equipment.
Solar panels have a wide range of applications, including remote power systems for cabins, telecommunications equipment, remote sensing, and, of course, electricity generation by commercial and residential solar electric systems.
We shall look at the background, development, and advantages of solar panels on this page.
We’ll study the construction, operation, and generation of solar power.
Table of Contents
A Short History Of Solar Panels
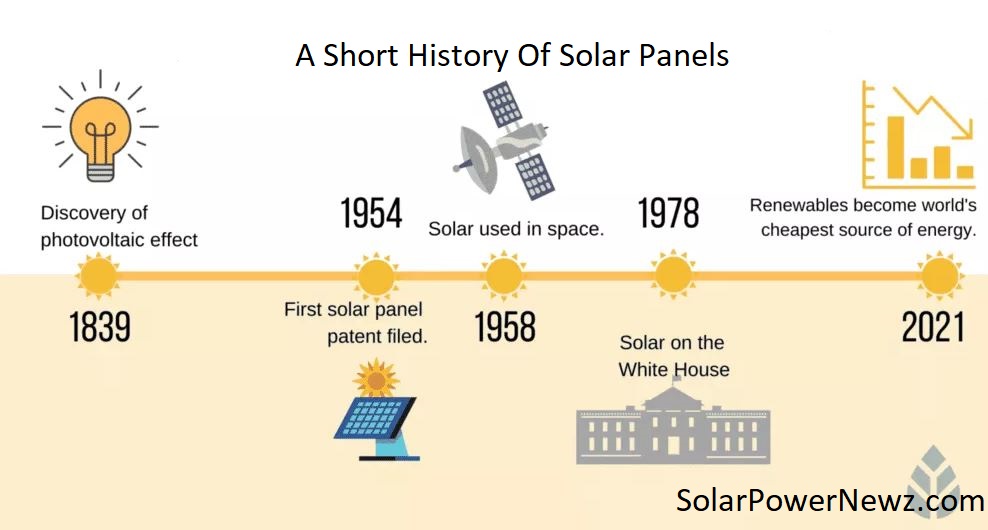
Solar energy has been developed for over a century. Solar energy was initially utilised mostly to generate steam, which could afterwards be used to power machinery. But it wasn’t until Edmond Becquerel discovered the “photovoltaic effect” that sunlight could be converted to solar electric energy.
Following Becquerel’s discovery, Charles Fritts built the first genuine solar cell in 1893 by coating sheets of selenium with a thin layer of gold. And from this humble beginning would arise the gadget we know today as the solar panel.
In 1941, Russel Ohl, an American inventor working at Bell Laboratories, produced the world’s first silicon solar cell. As a result of Ohl’s design, the same company created the first solar panel in 1954. Solar panels saw extensive use in spacecraft for the first time. In the 1970s, most people’s first solar panel was most likely installed in their new calculator!
Solar panels and solar panel systems are currently powering a variety of applications. Indeed, solar cells in the shape of panels are still employed in calculators. They are, however, being used to deliver solar electricity to large houses and business buildings, like as Google’s California headquarters.
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
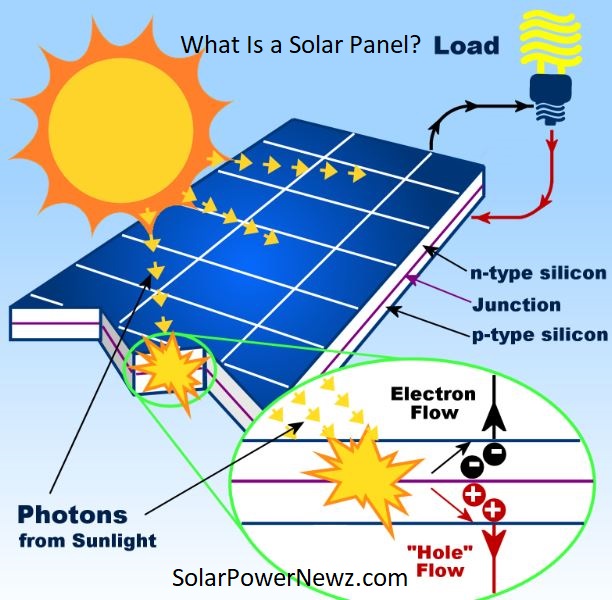
To put it simply, a solar panel generates energy by allowing photons, or light particles, to knock electrons free from atoms. Many smaller components called photovoltaic cells make up solar panels in reality.
(The method of converting sunlight into energy is simply known as “photovoltaic”).
Each solar cell is effectively a sandwich made of two slices of semi-conducting material, commonly silicon, the same material used in microelectronics.
Photovoltaic cells require an electric field to work. An electric field arises when opposite charges are separated, similar to how a magnetic field happens when opposite poles are separated. Manufacturers “dope” silicon with other substances to produce this field, which gives each sandwich slice a positive or negative electrical charge.
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types.
The addition of seed phosphorous to the top layer of silicon, in particular, adds extra electrons with a negative charge to that layer. Meanwhile, the bottom layer receives a boron treatment, resulting in fewer electrons and a positive charge.
All of this adds up to an electric field at the silicon layer crossing. Then, when a photon of sunlight knocks one electron free, the electric field will drive that electron out of the silicon junction.
Other components of the cell convert these electrons into useful power. Metal conductive plates on the sidewalls of the cell gather electrons and transport them to wires. Electrons can then flow freely, just like any other source of power.
1.3 microns thick, or about 1/100th the width of a human hair, and 20 times lighter than a sheet of office paper are the dimensions of the most recent ultrathin, flexible solar cells created by researchers.
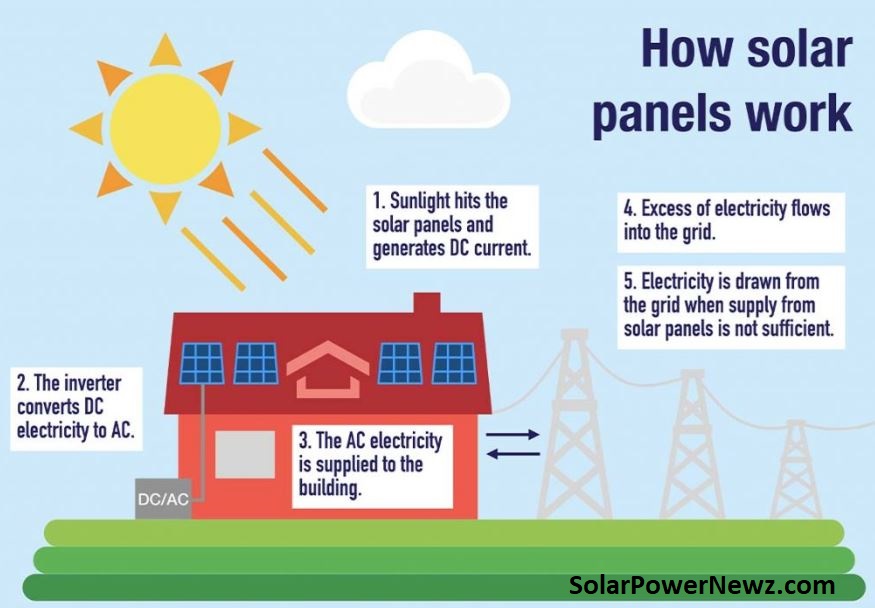
Sunlight is used by all solar energy systems to generate electricity, heat water, or air, however solar thermal and concentrated solar power (CSP) systems work differently from photovoltaic solar panels.
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types.
Types Of Solar Panel

TMonocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar panels are the three categories into which they are divided. Each kind has its own set of pros and limitations, and the ideal solar panel type for your installation will be determined by elements unique to your site and desired system features.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panel

These solar panels are manufactured from thin silicon wafers taken from artificially generated crystals. Single crystals formed in isolation aid in the formation of these cells, making them the most efficient.
They are the most expensive of the other groups as a result. Monocrystalline solar cells have an efficiency range of 15–24% but cost about 35% more than polycrystalline ones.
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panel

Polycrystalline solar panels are a newer discovery among the various varieties of solar panels, but they are gaining popularity and efficiency swiftly. Polycrystalline cells, like monocrystalline panels, are constructed of silicon. Polycrystalline cells, on the other hand, are formed by melting silicon crystal pieces.
The silicon crystal is placed in a vat of molten silicon during the production process. Instead of drawing it out gently, this crystal is allowed to fragment and then cool. After cooling in its mould, the fractured silicon is thinly sliced into polycrystalline solar wafers. These wafers are combined to produce a polycrystalline panel.
Polycrystalline cells are blue in hue because of the way sunlight reflects on the crystals. The reflection of sunlight off silicon bits differs from that of a clean silicon cell. Back frames and frames are often silver with polycrystalline, however this might vary.The structure of the cell is square, and there are no gaps between the corners of the cells.
Also In this article, we will discuss about How Does A Solar Panel Work, Solar Panel Types.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panel
Consider thin films if you’re seeking for a more cost-effective solution. Thin-film solar modules are created by depositing one or more photovoltaic films (often silicon, cadmium, or copper) over a substrate.
These solar module types are the simplest to manufacture and, thanks to economies of scale, cost less than alternatives since less material is needed to make them.
They are also flexible, which offers up many options for different uses and makes them less susceptible to high temperatures. The biggest drawback is that they take up a lot of area and are often unsuitable for household installations.
In addition, they give the shortest guarantees, as their lifespan is less than that of mono- and polycrystalline solar modules. They can, however, be a wonderful option for selecting between the various varieties of solar panels that have lots of room.
4. Amorphous Solar Panel

Amorphous solar cells are the most affordable type of solar cell. These are newly launched cells that are made in an unusual manner. They avoid using crystals. Instead, tiny silicon deposits on the backing substrate are used in their manufacturing process.
Amorphous solar cells have two primary advantages: flexibility in solar cells due to their incredibly thin silicon layer, and excellent efficiency in low light levels throughout the winter.
However, while these promise the aforementioned benefits, they also jeopardise efficiency. When compared to the other two versions, they provide the lowest efficiency rates of 7% – 9%. As a result, they require roughly double the panel size to produce the same output. They do not even have an industry-approved production process as of yet, thus they are less resilient than the other two types of solar panels.
5. Biohybrid Solar Panel

A hybrid solar cell combines monocrystalline and amorphous solar cells, hence it is not a fully solar cell. HET (heterojunction with intrinsic thin layer) solar cells are hybrid solar cells.
Due to the combination of the power of the two solar cells, the hybrid type is the most efficient when compared to each separate type of solar cell. These function best in warm weather, above 250 degrees Celsius. As a result, around 10% extra electricity is generated.
If the best is to be chosen, polycrystalline cells are the greatest choice for most installations because to their value for money, design, and efficiency rate.
FAQs.
What Is A Solar Panel?
The sun is the source of solar energy. Solar panels (also known as “PV panels”) are used to convert sunlight’s light, which is made up of energy particles known as “photons,” into electricity that may be utilised to power electrical loads.
Solar panels have a wide range of applications, including remote power systems for cabins, telecommunications equipment, remote sensing, and, of course, electricity generation by residential and commercial solar electric systems.
What Is A Solar Panel Easy Definition?
Solar panels are those gadgets that capture the sun’s rays and transform them into power or heat. A solar panel is essentially a group of solar (or photovoltaic) cells, which can be used to generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect. These cells are organised in a grid-like arrangement on the surface of solar panels.
What Is Solar Panel And How It Works?
Solar panels use photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors to concentrate solar radiation to turn sunlight into electrical energy. This energy can be converted into electricity or stored in batteries or thermal storage.
How Many Solar Panels Are Needed To Run A House?
A house with a monthly electricity demand of 1000 kWh requires 26 – 30 solar panels on average (Each solar panel is 320 watts).