Types of Solar Energy
In this article, we will discuss Types of Solar Energy. Solar energy systems come in a variety of configurations. Some are only for household use, while others are for large-scale commercial usage, while others generate heat and power. It is simple to divide the many types of solar energy systems into two categories: whether the sun’s direct energy is captured into heat energy or whether the sun’s energy is transformed into electrical energy.

When we say that the sun’s energy is converted into heat energy, we mean that the sunlight is essentially collected and used for heating. For example, when you leave a parked car in the sun all day and the interior heats up, or when the shallow end of a swimming pool becomes visibly warmer as it absorbs sunshine on a hot day. These methods of harnessing the sun’s heat can then be divided into two sorts of solar energy:
Table of Contents
Passive Solar Energy :– is the use of strategically aligned walls, windows, and architectural features — typically of a dwelling — designed to absorb and deflect solar radiation without the use of mechanical or electrical devices.
The purpose of passive solar heating is to lower the expense of electrical heating during the colder months of the year while keeping a home cooler during the warmer months.
The diagram below depicts a rudimentary model of a passive solar energy home.
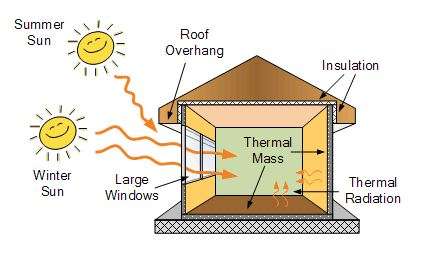
The passive solar heating diagram above is a general depiction of a house’s side that is strategically angled to absorb the sun’s heat in the winter and deflect the sun’s heat in the summer.
- Because it is higher in the sky when oriented with solar south, the sun labelled (1) is an example of a summer sun in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Summer solar rays are absorbed or reflected off the house’s uniquely built roof, keeping it cooler in the summer.
- The winter sun is higher in the sky.
- The strategically positioned windows of the house are designed to let in the heat of the winter sun, keeping the house warmer during the winder and, presumably, resulting in lesser energy consumption to heat your home.
Remember that the sun’s rays are not turned into electricity in passive solar heating.
Solar Energy that is Active :– The solar energy system is powered by an active electrical device, such as a water pump or an electrical power control box. Because of this necessity, an active solar energy system requires additional electricity, in addition to the sun, to run and maximise the system’s efficiency.
Active solar systems have benefits and drawbacks. The obvious advantage of the active system is that the external power source boosts the system’s efficiency. Another advantage is that it simplifies system control by providing controls to turn the machine on and off as well as to alter individual machine options such as temperature.
Active solar systems offer advantages and disadvantages. The obvious advantage of the active system is that the external power source increases the efficiency of the system. Another advantage is that it simplifies system control by allowing you to turn the machine on and off as well as change specific machine settings like temperature.
To create the heat required to raise the temperature of the water, a residential solar water heating system could use either photovoltaic solar panels or a concentrated solar power system.
There are several solar water heating systems; here is an example of a simple home solar water heating system.
This device is classified as active solar power since it requires a pump or another external mechanism to circulate water through the unit.
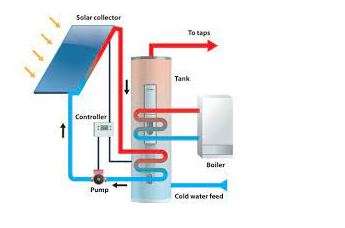
The diagram above depicts a household solar thermal system used to heat water. The solar water heater uses the heat from the sun to raise the temperature of your home’s water.
>> The water heater is connected to a source of chilled water.
>> Water is pumped through the solar thermal heater by a small pump that is powered by batteries or an electric source, and sometimes by the solar panel itself.
>> The controller, which can be installed in the home, is the mechanism that controls the system. The temperature and other parameters of the water heating system can be set by the controller.
>> The solar thermal panels, which are placed or attached to the home’s outside, gather the sun’s energy and use it to heat water to high temperatures.
>> The now-heated water is returned to the water heater.
>> The hot water is stored in the water heater until it is needed in the home. In the event that the panels do not receive enough sunlight to operate, the heater may be able to heat water on its own.
>> The water from the solar heater can now be sent to your home’s faucets.
Because the sun does not shine all night or every day, the solar water heater may still heat water using conventional on-grid electricity. When the sun shines, the on-grid electric power is turned off, and the water heater uses solar-heated water instead, saving your home energy and money.
A photovoltaic solar panel array installed atop a tracking system is another example of an active solar system. The solar panel’s tracking technology adjusts the panel’s face throughout the day to monitor the sun’s movement in the sky. These active tracking devices have the potential to significantly boost the efficiency of solar panels.
An active solar energy system, once again, is a solar power system that requires external energy to operate.
Using the Sun’s Energy to Produce Electricity: When the sun’s energy is turned into another form of energy, usually electricity, it falls into one of three categories of solar energy:
Photovoltaic Cells (PV): These cells generate electricity by using photons from the sun’s light. The vast majority of solar panels used today are photovoltaic cells. Discover how solar panels work.
Concentrated Solar Power – Solar Turbine: when the heat of the sun is transformed into electricity.
Each form of solar energy system operates differently, although they are all initially fueled by the sun’s heat or light energy.