What Exactly Is Biomass Energy?
In this article, we will discuss What Exactly Is Biomass Energy? The use of organic matter for energy production is referred to as biomass. When we talk about organic matter, we’re talking about live or recently living organisms. Wood, crops, animal manure, and even grass clippings may be included.
This page examines biomass in general, where it originates from, and how humans may use it. Continue reading to learn more about biomass.
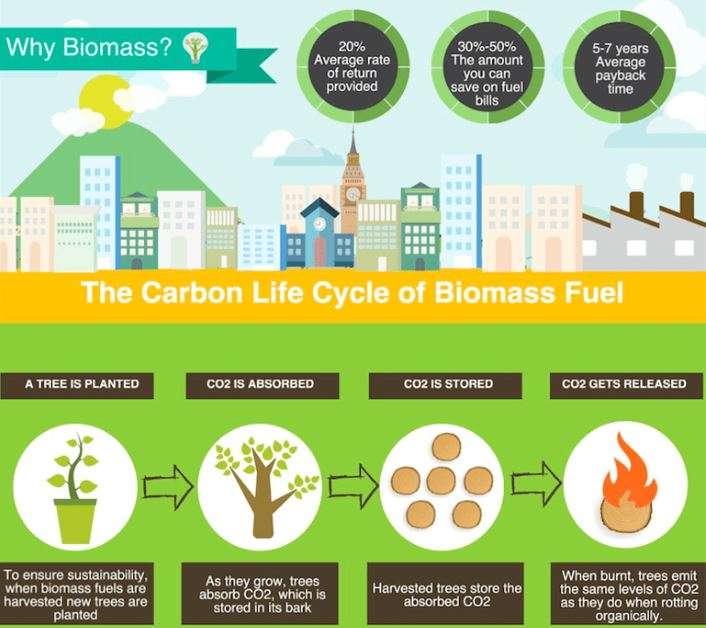
Table of Contents
The Main Sources of Biomass
Biomass energy (or bioenergy) can be generated from a variety of materials and byproducts, some of which may surprise you. Let us now look at the primary sources of biomass.
Animal Fats
You might be surprised to learn that animal fat can be utilised to generate biomass energy, but it’s real. Animal fat can be found in biodiesel, a type of biofuel. This is frequently simply one of several different chemicals included in fuel.
Sewage & Animal Waste
Yes, excrement can be used to generate biomass energy! Sewage and slurry (animal waste) can be utilised to generate biogas, a methane-rich gaseous fuel. Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion – more on this later.
Food Crops
Food crops can also be used to generate biomass energy. These are mostly used to make biofuels like bioethanol and biodiesel. The following are the most frequent ‘energy crops’ used in the biofuel industry:
- Wheat
- Corn
- Sugarcane
- Canola & Rapeseed
- Soybean
- Sunflower
Municipal Solid Waste
Did you know that some countries generate energy by burning municipal solid waste? This technique is known as Refuse Derived Fuel, or RDF for short.
While the RDF process differs greatly from that of biomass, the solid waste it employs is likely to contain some organic materials. Food and other waste products are examples of such things that, in theory, can be called biomass.
Wood
Biomass is most commonly obtained from wood. It is available in a variety of forms, all of which are ideal for Biomass energy production:
- Wood chips, sawdust, and clippings
- Tree bark, cut logs, and whole tree trunks
- Tree crops that grow quickly, such as willow and poplar.
The Different Types of Biomass Energy
As previously stated, there are numerous sources of biomass. These can be utilised in a variety of ways to generate various types of energy. Let us now look at the many sorts of biomass energy.
Biomass Power (Electricity)
Biomass power refers to the electricity generated by the combustion of biomass. The most common material utilised in this procedure is wood. It is burned to generate steam, which can then be used to turn a typical turbine to generate power.

This sort of biomass energy is mostly generated in large-scale facilities, such as purpose-built biomass plants. Some utilities have even converted conventional power facilities to run entirely on biomass. Others have built infrastructure to burn both fossil fuels and biomass, a process known as co-firing.
Biomass Fuels
Biomass fuel (biofuel) is a type of biomass energy derived primarily from food crops and animal fats. Bioethanol and biodiesel are the two most common types of biofuel.
The most popular type of biofuel is bioethanol. It is a type of alcohol fuel made mostly from wheat, corn, sugarcane, and other starchy crops like potatoes.
The other type of biofuel is biodiesel, which is typically generated from animal fats and vegetable oils. Because it is more expensive to make, it is less prevalent than bioethanol.

While bioethanol and biodiesel can be used on their own, they are most often blended with petroleum fuels such as gasoline (for bioethanol) and diesel fuel (for biodiesel) (for biodiesel).
Biogas
Biogas is the third most common type of biomass energy. This is created through the breakdown of organic materials, which is generally done in an anaerobic digester. While this can theoretically be classified as a biofuel, we shall describe it separately here.
The anaerobic digestion (AD) process eliminates oxygen from a sealed container containing biomass materials. This is then heated in order to hasten the decomposition of the biomass. Methane is emitted during the decomposition process and then captured for subsequent use.
Biogas is usually used for heating and cooking, but it can also be used as a transportation fuel source.
Is Biomass Safe for the Environment?
The quick answer is that biomass is considered an environmentally benign source of energy. This is because biomass is carbon neutral; it absorbs carbon while growing and then releases it back into the atmosphere when burned.
It is critical to note that, while biomass energy production is carbon neutral, RDF is not. This is because municipal trash streams are likely to have a high concentration of non-organic substances such as plastics.
Overview
So there you have it, the definition of biomass energy. Biomass energy production employs organic material in a variety of methods. It can generate power, liquid fuels, and even a type of natural gas. Biomass is produced by energy crops, plants, and animals.
Biomass is widely regarded as one of the most environmentally benign energy sources available. While it does not compare to more mainstream renewable energy sources (such as solar and wind), it is critical in assisting in the reduction of the net level of greenhouse emissions we emit each year.