What is a Wind Turbine?
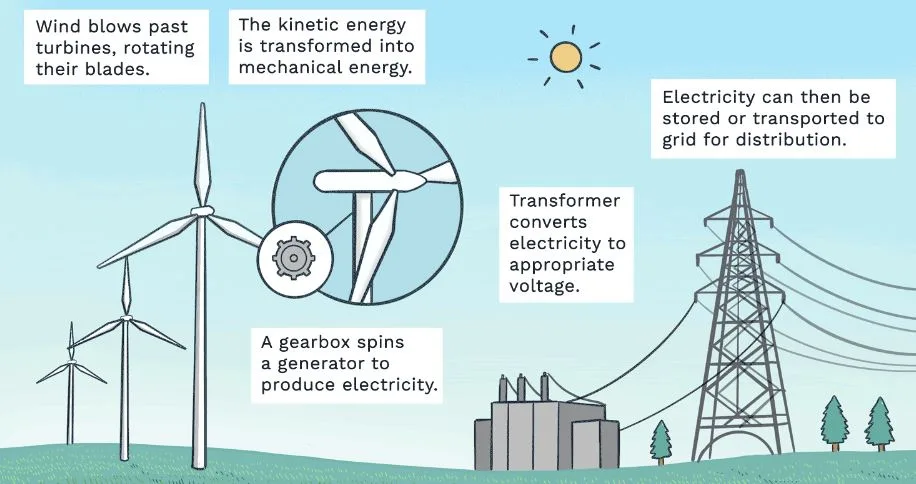
In this article we will discuss about What is a Wind Turbine, How Do Wind Turbines Produce Electricity. Wind turbines are an outgrowth of the traditional windmills observed in more rural regions around the world. Their goal is to lessen reliance on fossil fuels for energy generation while also producing energy in a less wasteful manner. They work by harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind, which propels the turbine’s blades and spins a motor, which turns the kinetic energy into electrical energy for consumer use.
Wind turbines are rotating machines that can be used for grinding or to generate electricity using the kinetic energy of the wind. They offer us with clean, renewable energy for both our house and office. Wind turbines are an excellent method to save money while also keeping the environment clean and green.
This method has been developed for use in a variety of applications, including boats, traffic signs, and entire cities powered by a wind farm. The creation of wind turbines is a significant step toward revolutionising the way we generate energy.
Wind generators are classified into two types: those with vertical axes and those with horizontal axes. They may generate electricity both on and off the grid. Wind turbines can be clustered together to form “wind farms,” which are utilised as backup power by major corporations. They can be used for grain grinding, water pumping, and battery charging in addition to generating energy.
Wind turbines were formerly utilised for sailing, irrigation, and grain grinding. It was employed to generate power in the early twentieth century. Large wind turbines can now be found in rural locations or near the sea coast, where the wind speed varies throughout the day. Wind resource assessment is a device used to estimate wind speed.
Table of Contents
Wind Turbine Components
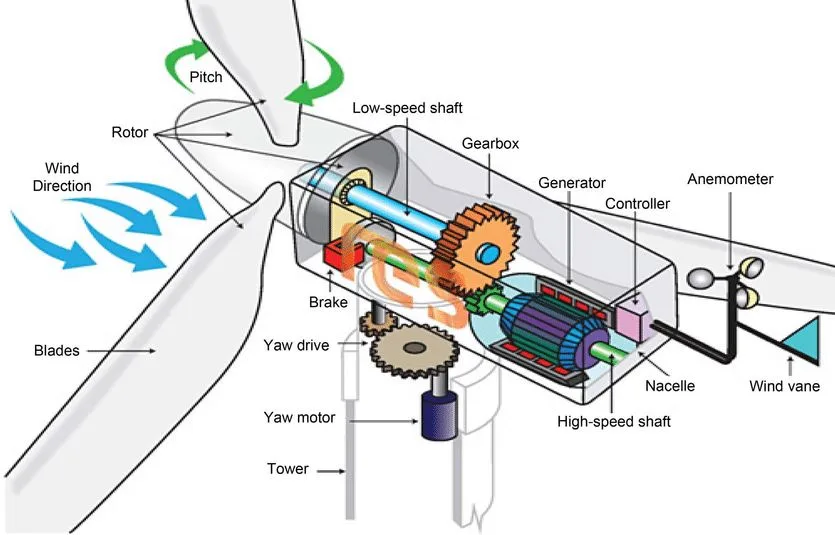
Wind turbine systems are made up of numerous pieces of equipment that all work together to supply electricity where it is needed. The list below serves as a broad blueprint for the primary components that can and frequently will be found in wind turbine systems regardless of the type of design.

- Rotor – The rotor is made up of blades that are connected to a hub. The blades are shaped such that when the wind pushes against them they turn
- Pitch Drive – Used to rotate blades to accommodate for high-speed wind
- Nacelle – The rotor is attached to a housing unit called a nacelle, which protects various other components necessary to the wind turbine operation
- Brake – It is necessary to slow down the rotor.
- Low-Speed Shaft – Attaches to the rotor and rotates in a 1:1 ratio with it.
- Gear Box – Serves the same function as a car, the rotor spins slowly as the wind pushes against it and the gearbox or transmission increases that rotational speed for the generator
- High-Speed Shaft – Attached to the gearbox and generator, it rotates faster than the rotor or low-speed shaft.
- Generator – The actual process for converting rotating kinetic energy to electricity.
- Wind Vane – Detects wind direction and adjusts the rotor and nacelle accordingly.
- Yaw Drive – Keeps the rotor and therefore the turbines facing the wind
- Tower – Elevates the aforementioned components to an altitude that optimizes wind exposure
In this article we will discuss about What is a Wind Turbine, How Do Wind Turbines Produce Electricity.
How Do Wind Turbines Work?
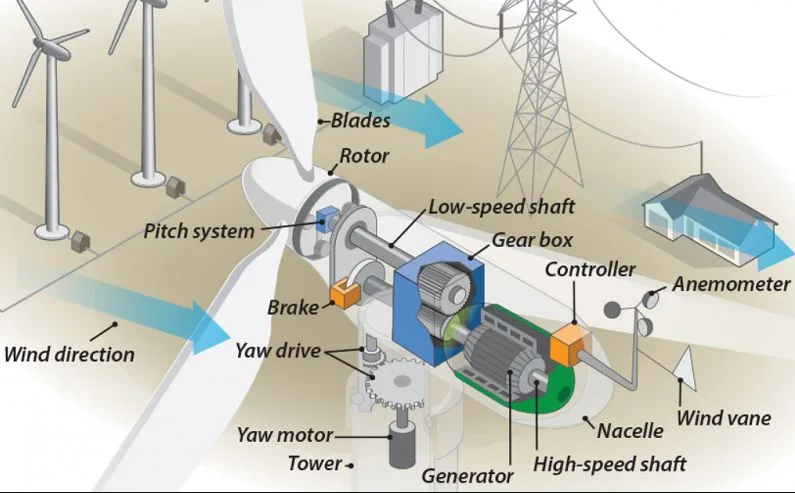
Wind turbines run on a system comprised of numerous key components that convert kinetic wind energy into electrical energy. Wind turbine systems of all types operate on the same principle that allows a generator to generate power. This principle states that if magnets are rotated around a wire coil or a wire coil rotates within a magnetic field quickly enough, electricity is created.
The generator is a complex system of magnets and conductors. Using the wind to move the blades generates the force required to turn the magnets or conductor coil, which produces electricity. The following is a step-by-step process that demonstrates how a wind turbine generates power.
- A tower is built to place the wind turbine system at the proper altitude, where wind travels at a faster and more consistent rate.
- Rotor blades are exposed to wind, which causes them to turn.
- The low-speed shaft, which is coupled to a gearbox, spins at the same rate as the rotor.
- The gearbox converts this slow rotating speed into a quicker rotational speed by using proper gearing.
- The high-speed shaft, which is attached to a generator at the gearbox’s outgoing end, spins at a faster pace.
- The generator spins at such a fast pace that magnets are spun around a coil of metal wire, generating electricity.
- The electricity is transmitted from the generator via cables to the required applications, which could be direct appliances or a battery.
Here is an infographic on how wind turbines function that will help you comprehend the various wind turbine components.
Types of Wind Turbines
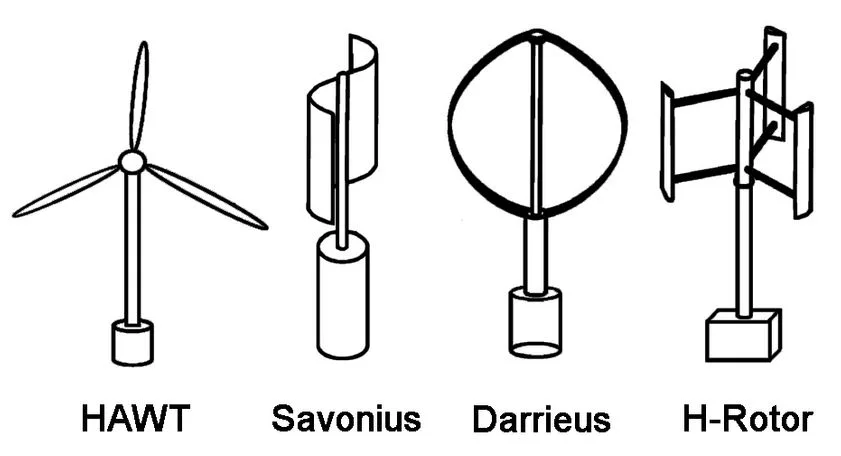
In the wind energy sector today, there are two primary types of wind turbines that may be seen in design and implementation. The first and most frequent kind is the horizontal axis wind turbine, which is powered by a horizontal shaft that runs perpendicular to the vertically spinning blades. These wind turbine technologies can be found in both large wind farms and small-scale operations.
The vertical axis wind turbine is a second form that is less widespread in the wind energy business. The vertical axis turbine, as one might expect, has a vertical shaft to which the blades or rotor are attached and rotate horizontally. The vertical axis wind turbine comes in a variety of configurations, but the key advantage is that maintenance is simplified because the gearbox and generator are more accessible.
- Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine – This is the most common type of wind turbine, with a horizontal low-speed shaft connecting to the rotor. There are several ways to build this wind turbine, but they all follow the same concept as described above. The rotor spins with the wind, converting rotational kinetic energy to electrical energy via a generator.
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbine – This form of wind turbine is less prevalent, although it has the advantage of not requiring the rotor to face into the wind. The shaft that connects to the rotor is vertical, and the gearbox and generator are located near the bottom of the tower. There are many different types of vertical axis wind turbines, all of which use force along the X-axis (parallel to the ground) as opposed to force along the Y-axis in horizontal axis turbines (perpendicular to the ground).
The following are many versions of vertical axis wind turbine systems. Many of these were designed decades ago and are no longer in use; nevertheless, the designs for these have been updated and altered so that newer models that are more efficient and have fewer difficulties than the older ones can be developed.
a. Darrieus Wind Turbine – This vertical axis wind turbine employs curved blades that rotate and generate internal wind force, allowing the rotor to spin at high rates independent of wind speed. The disadvantage is that this turbine typically requires an external motor to begin spinning.
b. Giromill – An H-shaped rotor is used in this Darrieus Wind Turbine variant. The giromill, on the other hand, has straight blades that run parallel to the shaft. Aside from that, they function on the exact same principle.
c. Cycloturbine – A giromill that not only features straight blades that run vertically, but also allows the straight blade to rotate about its central axis. The benefit of this type of turbine is that it produces the maximum power and can self-start (start without any external assistance).
d. Savonius Wind Turbine – The operation of this vertical axis wind turbine is based on the principles of drag and wind resistance. The blades are in the shape of an S, with the two curved portions rotating with the wind. Because the curved section provides less drag, the rotor can spin. These turbines produce little electricity.
e. Vortexis Wind Turbine – This is the most recent advancement in vertical axis wind turbine technology. It has been used by special forces in Afghanistan and Iraq to power their equipment. This turbine contains two sets of blades, one smaller set that sits in a circle and one larger set that surrounds the smaller set in a larger circle, acting like a gearbox. The outer set of blades spin in response to the wind, and by doing so, they force their own wind to turn the smaller inner set of blades. These blades are attached to a shaft, which turns a generator.