What Is Geothermal Energy?
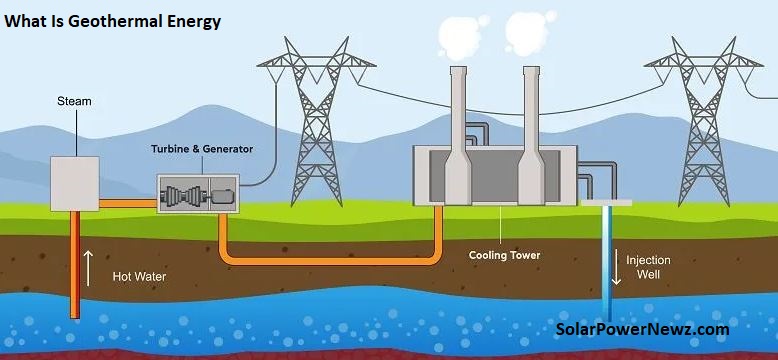
Geothermal energy is heat found in the earth. The Greek terms geo (earth) and therme are where the word geothermal comes from (heat). Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source since heat is constantly created within the earth. Geothermal heat is used to bathe, heat homes, and generate electricity.
In this article we will discuss about What Is Geothermal Energy, Uses and Effect.
Geothermal energy is the term used to describe heat that is taken from the earth’s crust. It can be found in rocks and fluids beneath the crust as deep as the earth’s boiling molten rock, magma.
Wells are dug a mile underground to obtain steam and hot water, which can subsequently be utilised to power turbines coupled to electricity generators. Geothermal power facilities are classified into three types: dry steam, flash, and binary.
The oldest form of geothermal technology, dry steam, extracts steam from the earth and utilises it to directly drive a turbine. Flash plants convert high-pressure hot water to cool, low-pressure water, whereas binary plants convert hot water to vapour by passing it through a second liquid with a lower boiling point.
Table of Contents
Geothermal energy is generated deep within the earth.
Geothermal energy is produced by the slow disintegration of radioactive particles in the earth’s core, a process that occurs in all rocks.
The earth is divided into four major divisions or layers:
- A solid iron inner core roughly 1,500 kilometres in circumference.
- An outer core of hot molten rock known as magma that is approximately 1,500 miles thick.
- A 1,800-mile-thick mantle of magma and rock surrounds the outer core.
- A crust of solid rock that creates the continents and ocean floors that is 15 to 35 miles thick under the continents and 3 to 5 miles thick under the oceans.
Scientists determined that the temperature of the earth’s inner core is approximately 10,800 degrees Fahrenheit (°F), which is as hot as the sun’s surface. Temperatures in the earth’s mantle range from around 392°F at the upper border with the crust to roughly 7,230°F at the mantle-core boundary.
The earth’s crust is divided into sections known as tectonic plates. Many volcanoes form when magma gets close to the earth’s surface near the boundaries of these plates. Volcanic lava is partially composed of magma. Deep underground, rocks and water absorb heat from magma. Deeper beneath, the rocks and water have the highest temperatures.
Is Geothermal Energy Renewable?
Yes, because its source is the nearly limitless heat created by the Earth’s core. Even in geothermal areas that rely on a hot water reservoir, the volume extracted can be reinjected, making it a sustainable energy source.
Geothermal Power Plant
Icelandic geothermal power plant (flash steam, mixed cycle). Geothermal power plants create electricity by utilising geothermal energy (the Earth’s inherent thermal energy). The only difference between them and coal or nuclear power plants is the heat source.
Hydrothermal resources (water and heat) are used in geothermal power plants (thermal). Geothermal power plants require high-temperature hydrothermal resources (300°F to 700°F) derived from either dry steam wells or hot water wells.
These resources are used by drilling wells into the ground and then piping steam or hot water to the surface. The heated water or steam drives a turbine, which produces electricity. Some geothermal wells can reach depths of up to two miles.
Types Of Geothermal Power Plants
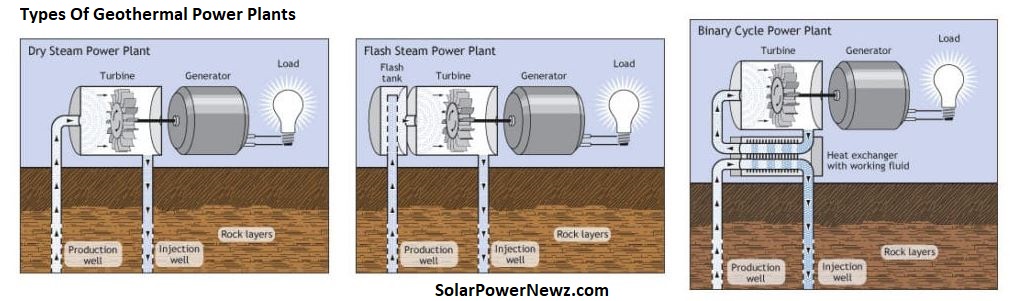
There are three types of geothermal power plants:
- Dry steam plants employ geothermal reservoir steam to operate generator turbines. In 1904 in Tuscany, Italy, the first geothermal power plant was created, when natural steam erupted from the earth.
- Flash steam plants generate steam by converting high-pressure hot water from deep inside the earth. When the steam cools, it condenses into water, which is then injected back into the earth and reused. Flash steam is used in the majority of geothermal power facilities.
- Heat is transferred from geothermal hot water to another liquid in binary cycle power plants. The heat converts the second liquid to steam, which powers a generator turbine.
Use Of Geothermal Energy
Some geothermal energy applications use temperatures near the earth’s surface, while others involve digging kilometres under the earth. Geothermal energy systems are classified into three types:
- Direct use and district heating systems
- Geothermal power plants
- Geothermal heat pumps
1. Direct Use And District Heating Systems
Direct use and district heating systems draw hot water from springs or reservoirs near the earth’s surface. Ancient Roman, Chinese, and Native American cultures all made use of hot mineral springs for bathing, heating, and cooking.
Many hot springs are still used for bathing today, and many people believe the hot, mineral-rich waters are beneficial to their health.
Geothermal energy is also used to directly heat individual buildings and to heat several structures via district heating systems. Buildings are heated by hot water that is heated close to the earth’s surface. The majority of the buildings in Reykjavik, Iceland, are heated by a district heating system.
Geothermal energy has industrial applications such as food dehydration (drying), gold mining, and milk pasteurisation.
2. Geothermal Electricity Generation
Water or steam at high temperatures (300° to 700°F) is required for geothermal electricity generation. Geothermal power stations are often developed where geothermal reservoirs are located, within a mile or two of the earth’s surface.
3. Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps heat and cool buildings by taking use of the steady temperatures near the earth’s surface. During the winter, geothermal heat pumps transmit heat from the ground (or water) into buildings and reverse the process in the summer.
Advantages Of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy has a lot of advantages, but there are also some challenges that must be overcome if this renewable resource is to be used to its full potential.
1. Environmentally Friendly
Geothermal energy has a smaller environmental impact than traditional fuels like coal and other fossil fuels. A geothermal power plant’s carbon footprint is also quite small. Although geothermal energy pollutes, it does so very infrequently compared to fossil fuels.
2. Renewable
The planet is expected to be destroyed by the sun in 5 billion years, at which point geothermal energy will still be a viable source of energy. The earth’s hot reservoirs are renewable and sustainable since they replenish naturally.
3. Huge Potential
Only 15 terawatts of energy are currently consumed globally, which is a minuscule portion of the potential energy from geothermal sources.
There is hope that as industrial research and development continue, more viable geothermal resources will become available even if the majority of reservoirs are currently unsuitable.
It is estimated that geothermal power plants can generate between 0.0035 and 2 terawatts of energy.
4. Sustainable/Stable
Compared to other renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, geothermal energy is a dependable source of energy. This is due to the fact that the resource is always accessible, unlike wind or solar energy.
5. Heating And Cooling
Turbines must be driven by water that is over 150 °C in order to effectively exploit geothermal energy to generate power. An alternative is to use the temperature difference between the soil source and the surface.
Just two metres below the surface, a geothermal heat pump can operate as a heat sink/source since the ground is more resistant to seasonal heat variations than the air.
6. Reliable
Due to its stability as opposed to other energy sources like the sun and wind, this resource’s energy output is simple to compute. As a result, we can accurately forecast how well a geothermal system will function.
7. No Fuel Required
There is no need for fuel because geothermal energy is a naturally existing resource. In contrast, fossil fuels are limited resources that must be mined or otherwise removed from the earth.
8. Rapid Evolution
The substantial geothermal research that is currently being done is leading to the development of new technologies that will improve the energy process. To expand and diversify this industry, numerous projects are being launched. Many of the current constraints of geothermal energy are being reduced as a result of this quick progress.
Disadvantages Of Geothermal Energy
1. Location Restricted
The fact that geothermal energy is site-specific is its main drawback. Some areas cannot exploit this resource since geothermal plants must be constructed where the energy is available.
Naturally, this is not an issue if you reside somewhere where geothermal energy is widely available, like Iceland.
2. Environmental Side Effects
Despite the fact that geothermal energy rarely releases greenhouse gases, when digging they are typically released into the atmosphere because of the underground storage of these gases. The rate of these gas emissions into the atmosphere is higher near geothermal plants, despite the fact that they also occur naturally. But even so, these gas emissions are considerably lower than those caused by fossil fuels.
3. Earthquakes
The utilisation of geothermal energy may result in earthquakes. This is due to the trench’s influence on the geological makeup of the earth. Modern geothermal power plants that pump water into the earth’s crust to widen cracks and boost resource extraction are particularly prone to this problem.
However, because most geothermal systems are not located close to populated areas, the effects of these earthquakes are minimal.
4. High Costs
The cost of geothermal energy is high. A system with a 1 megawatt capacity costs between $2 million and $7 million US. In contrast, if the initial outlay is substantial, the cost may be amortised as a long-term investment.
5. Sustainability
The liquid must be injected back into the subsurface reservoirs faster than it is used up in order to keep geothermal energy sustainable. This means that in order to ensure the sustainability of geothermal energy, adequate management is required.
FAQs.
Is Geothermal Energy Renewable?
Yes, because the almost infinite amount of heat produced by the Earth’s core serves as its source. The volume extracted from geothermal locations that rely on a hot water reservoir can be reinjected, making it a sustainable energy source.
How Does A Geothermal Energy Works?
Steam is used in geothermal power plants to create energy. The hot water reservoirs that produce the steam can be found many miles or more below the surface of the planet. A generator is turned on by the steam, which also drives a turbine.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Geothermal Energy?
- Limitations on location. The fact that geothermal energy is location-specific is its biggest drawback.
- Side effects on the environment.
- Earthquakes.
- Sustainability at High Costs.
Why Is It Bad To Use Geothermal Energy?
Cons of geothermal energy include the production of waste, the need for proper reservoir management, location-specificity, high initial cost, and the potential for earthquakes in extreme circumstances. Geothermal energy has the potential to be a significant worldwide energy source, but is currently constrained by high initial costs.
Is Geothermal Energy A Good Idea?
Geothermal energy, according to experts, can lessen our reliance on foreign oil while being greener, more cost-effective, and more efficient than burning fossil fuels. … Because they can operate constantly, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, geothermal plants are also thought to be more dependable than coal or nuclear reactors.
What Are 3 Main Uses Of Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy can be used to heat, cool, and generate electricity. Depending on the resource and technology used, geothermal energy can be utilised to heat and cool buildings with geothermal heat pumps, generate electricity with geothermal power plants, or directly heat structures.
What Are The 3 Ways To Get Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy systems can be divided into three primary categories:
systems for district heating and direct usage.
geothermal energy facilities.
pumps for geothermal heat.
How Long Does Geothermal Last?
How durable are geothermal heat pumps? Geothermal heat pumps have a much longer lifespan than standard equipment. They last 20 to 25 years on average. On the other hand, standard furnaces typically last 15 to 20 years, and central air conditioners 10 to 15 years.
Why Is Geothermal Energy A Renewable Resource?
because the almost infinite quantity of heat produced by the Earth’s core is its source. The volume extracted from geothermal locations that rely on a hot water reservoir can be reinjected, making it a sustainable energy source.