What Is Nuclear Energy?
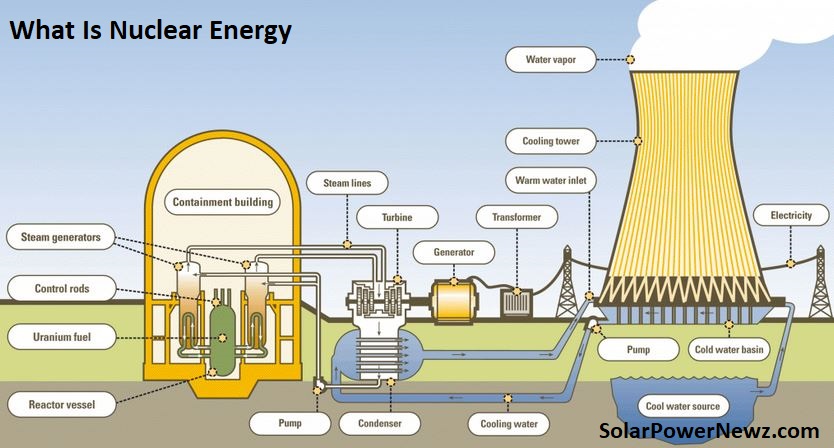
Nuclear energy is created by splitting atoms in a reactor in order to heat water into steam, operate a turbine, and generate electricity. Ninety-three nuclear reactors in 28 states produce roughly 20% of the nation’s electricity while emitting no carbon dioxide since reactors use uranium rather than fossil fuels. These plants are always on: well-maintained to avoid outages and built to resist extreme weather, they support the grid 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
In this article we will discuss about What Is Nuclear Energy, Working, Pros, And Cons.
Nuclear energy is a type of energy emitted by the nucleus, the centre of an atom composed of protons and neutrons. This type of energy can be generated in two ways: fission (when atom nuclei divide into numerous portions) or fusion (when nuclei combine).
Nuclear fission is the sort of nuclear energy that is being used to generate electricity around the world, whereas fusion technology is still in the works. Today, over 400 commercial reactors are in operation in over 30 nations.
Nuclear power is the only type of electricity that can consistently deliver a constant supply of power known as baseload power while producing no greenhouse gases. Nuclear energy has one of the least negative environmental impacts on land and natural resources of any energy source.
Table of Contents
What Is Fission?
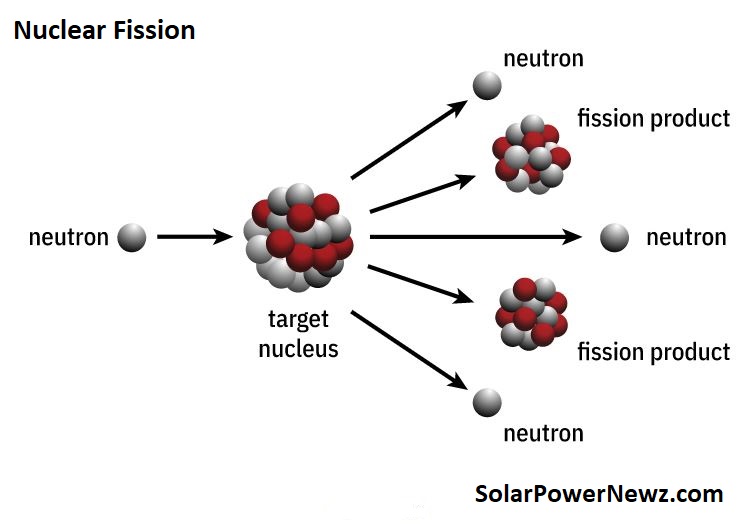
Fission occurs when a neutron collides with a larger atom, causing it to excite and split into two smaller atoms known as fission products. There is a release of more neutrons, which could start a chain reaction.
A significant quantity of energy is released during atom splitting.
Uranium and plutonium are the most widely used fission fuels in nuclear power reactors because they are easy to start and manage.
What Is Fusion?

The underlying chemical and physical processes that we use every day to create energy are what we all rely on. This has primarily been accomplished throughout history by burning carbon-based resources like wood, coal, and gas or by using the sun, wind, and water to generate energy.
Currently, fission and fusion are the two processes used to create nuclear energy. Comparatively speaking, fusion reactions are more challenging to control. For this reason, fission processes are the primary means by which nuclear power plants produce energy and electricity.
Atoms are used in two physical processes, fusion and fission, to produce enormous amounts of energy. More energy is produced by them than by other nuclear processes by a factor of a million.
What Is The Difference Between Fission And Fusion?
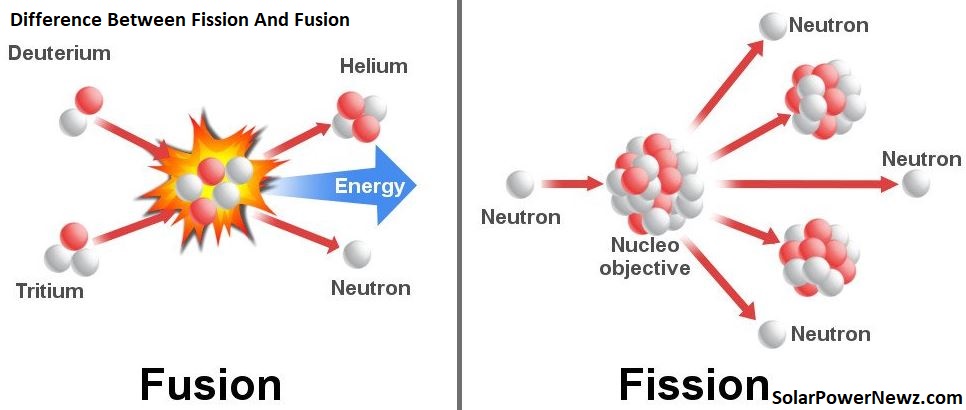
All of the energy we generate is derived from fundamental chemical and physical processes. Throughout history, this has largely been accomplished by burning carbon-based resources such as wood, coal, and gas, or by harnessing power from the sun, wind, and water.
There are currently two methods for producing nuclear energy: fission and fusion. Fusion reactions are more difficult to regulate than fission reactions. This is why all nuclear power plants generate energy and electricity through fission processes.
Fission and fusion are two physical processes that use atoms to generate large amounts of energy. Compared to other nuclear reactions, they generate energy on a scale of millions.
How Does Nuclear Energy Work?
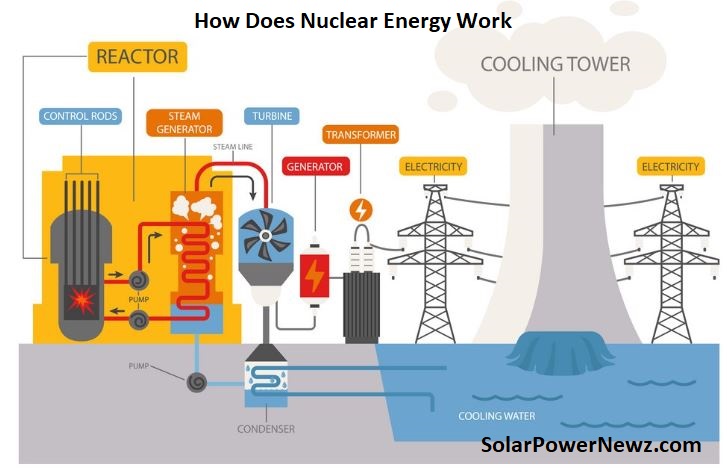
Nuclear energy is created by breaking uranium atoms, a process known as fission. This produces heat, which is then converted into steam and used by a turbine generator to generate power. Nuclear power plants produce no greenhouse gases since they do not consume fuel.
A nuclear reactor generates electricity in the same way that other power plants do. The chain reaction generates energy, which converts water to steam. Steam pressure powers a generator, which produces energy.
The distinction is in how heat is generated. To generate heat, fossil-fuel power plants burn coal, oil, or natural gas. A nuclear power plant generates heat by separating atoms, a process known as nuclear fission.
In a Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) the type of reactor being developed in the UAE high pressure prevents water in the reactor vessel from boiling. The superheated water is transferred to a steam generator via a network of small pipes.
The heat in these pipes is utilised to convert a second, isolated source of water to steam, which drives the turbine. The reactor water is poured back into the reactor vessel and warmed. The turbine’s steam is cooled in a condenser, and the resulting water is returned to the steam generator.
Pros And Cons Of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Energy Pros
Nuclear energy has various advantages and disadvantages, and it is critical to comprehend both sides in order to appreciate what this energy resource is capable of. Knowing the benefits and drawbacks of nuclear energy will allow you to determine for yourself if this energy source is a good choice for our future energy requirements and the environment.
1. Low Cost Of Operation
After the initial building costs, nuclear energy is one of the most cost-effective energy solutions accessible. Unless those resources are located near the power plant they supply, the cost of producing electricity from nuclear energy is substantially cheaper than the cost of producing energy from gas, coal, or oil.
Nuclear energy also has the advantage of experiencing very minimal risks of cost inflation, as opposed to traditional fossil fuels, which often fluctuate in price.
2. Reliable Source Of Energy
While certain energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are affected by weather conditions, nuclear energy is not. It doesn’t matter if the wind isn’t blowing or if the day is gloomy. Nuclear power plants are largely unaffected by external environmental conditions, producing predictable and consistent energy output.
A nuclear power plant in full operation may produce electricity nonstop for a whole year, allowing for a favourable return on investment due to no energy production delays.
Nuclear power plants are also reliable since we have enough uranium on the earth to supply energy for the next 70-80 years. While that may not appear to be a long period, it is longer than many fossil fuels are expected to survive, and other nuclear energy sources are being investigated for use in nuclear power plants.
3. Stable Base Load Energy
You might not realise it, but nuclear energy is widely used in the United States. It accounts for around 20% of all electricity generated in the United States.
This efficient energy source is provided by the 98 nuclear power reactors located in 30 different states around the United States. Because nuclear power plants produce reliable power, it is perfect for usage in conjunction with other kinds of renewable energy.
Wind turbines, for example, create huge amounts of power when the wind blows. When the wind blows, nuclear facilities can reduce their electricity output. When the wind isn’t blowing and more energy is required, nuclear energy can be modified to compensate for the lack of wind (or solar) generated power.
4. Produces Low Pollution
It is clear that nuclear energy has both benefits and drawbacks in terms of pollution; don’t worry, we’ll discuss nuclear waste momentarily. However, the overall pollution output from a nuclear power plant is quite low when compared to energy production from fossil fuels.
Currently, using nuclear energy reduces carbon emissions by around 555 million metric tonnes annually. This decrease in greenhouse gas emissions is a great example of how moving to nuclear power might lessen our long-term contribution to climate change.
5. It Has High Energy Densit
On our list of Pros And Cons of nuclear energy, one pro stands out particularly. Nuclear fission, the process used to create nuclear energy, generates a lot more energy than simply burning coal, gas, or other fossil fuels.
How much more powerfully? Nearly 8,000 times more energy is produced by nuclear fission than by conventional fossil fuels. That has a substantial energy density. Nuclear energy produces less waste because it is more waste-efficient than other forms of energy
Nuclear Energy Cons
We’ve explored what makes nuclear energy a wonderful alternative for the future of our electricity needs in our list of nuclear energy advantages and downsides. However, there are some drawbacks to nuclear energy that should be considered while deciding whether it is the best form of ecologically responsible energy for our future. Here are some of the major disadvantages of nuclear energy.
1. Expensive To Build
Nuclear power facilities are extremely expensive to build, despite the fact that they are quite affordable to operate—and the cost is rising. The expected cost of building a nuclear plant increased from $2-$4 billion to $9 billion between 2002 and 2008, and power plants frequently exceed their cost projections during construction.
In addition to the expense of developing a power plant, nuclear facilities must also commit expenditures to secure the waste they produce and keep it in cooled structures with security protocols in place. All of these expenditures add together to make nuclear power prohibitively expensive.
2. Accidents
The Chernobyl accident is one of the first things that most people think of when they hear the term nuclear power plant. Although we don’t know how many people perished as a result of the Chernobyl disaster, it’s estimated that up to 10,000 people died as a result of the long-term effects of radioactivity in the region.
The Fukushima nuclear power plant disaster in 2011 demonstrated that accidents can and do occur, regardless of how safe nuclear power facilities are planned to be.
3. Produces Radioactive Waste
Although nuclear energy production produces no emissions, it does generate radioactive waste, which must be carefully stored to avoid polluting the environment.
While radiation may appear to be frightening, humans are constantly exposed to trace amounts of radioactivity from cosmic rays or radon in the air we breathe. Radiation is not toxic in small doses, but radioactive waste from nuclear energy production is extremely dangerous.
The storage of radioactive waste is a significant concern for nuclear power plants. Because nuclear waste cannot be destroyed, the current option is to secure it in containers and deposit it far below, where it cannot harm the environment. As technology advances, we hope to develop better ways to store radioactive waste in the future.
4. Impact On The Environment
Nuclear power facilities have a bigger environmental impact than merely the trash they generate. Uranium mining and enrichment are not ecologically favourable operations. Open-pit uranium mining is safe for miners, but it produces radioactive particles, causes erosion, and even pollutes adjacent water sources.
Underground mining is no better, exposing miners to high levels of radiation while creating radioactive waste rock during extraction and processing.
5. Security Threat
Because it is fuelled by nuclear energy, nuclear power poses a unique threat to our national security. Terrorists may target nuclear power stations in order to cause a disaster, and the uranium used to generate the power can be converted into nuclear weapons if it falls into the wrong hands. For these reasons, the security of nuclear materials and nuclear power facilities is critical.
6. Limited Fuel Supply
There are certainly significant advantages and disadvantages to nuclear energy, but one of the most crucial aspects to bear in mind is that nuclear energy is dependent on uranium and thorium to generate electricity.
We will be unable to generate electricity using the nuclear power plants we have built for the future unless we can achieve nuclear fusion or build breeder reactors before our supply runs out. Finally, nuclear power is simply a short-term option at a great cost.
FAQs.
What Is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy is created by splitting atoms in a reactor in order to heat water into steam, operate a turbine, and generate electricity. Ninety-three nuclear reactors in 28 states produce roughly 20% of the nation’s electricity while emitting no carbon dioxide since reactors use uranium rather than fossil fuels.
How does nuclear energy work?
Nuclear energy is created by breaking uranium atoms, a process known as fission. This generates heat, which is used to make steam, which is then used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Nuclear power facilities emit no greenhouse gases since they do not burn fuel.
What Are the Advantages of Nuclear Energy?
The advantages of nuclear power are:
1. One of the most low-carbon energy sources.
2. It also has one of the smallest carbon footprints.
3. It’s one of the answers to the energy gap.
4. It is crucial to how we respond to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
5. Reliable and cost-effective.