What Is Solar Energy?

The conversion of solar energy into thermal or electrical energy is known as solar power. Solar technology can use this energy to generate electricity, provide light or a warm interior atmosphere, and heat water for domestic, commercial, or industrial use.
In this article we will discuss about What Is Solar Energy, Definition, Types, & Working.
Solar energy is the cleanest and most abundant renewable energy source available, and the United States has some of the most abundant solar resources in the world. Solar energy is a versatile energy source that may be used to heat, cool, and light houses and businesses.
In one hour, more energy from the sun falls on the earth than everyone on the planet uses in a year. A multitude of methods are used to turn sunlight into useable energy for structures. The most common solar technologies for houses and businesses include solar photovoltaics for energy, passive solar design for space heating and cooling, and solar water heating.
Businesses and industries employ solar solutions to diversify their energy sources, improve efficiency, and save money. Solar photovoltaic and concentrating solar power technologies are used by energy producers and utilities to generate electricity on a large scale to power cities and small towns.
Table of Contents
What Is Solar Energy, Definition, Types, & Working
How Does Solar Energy Work?
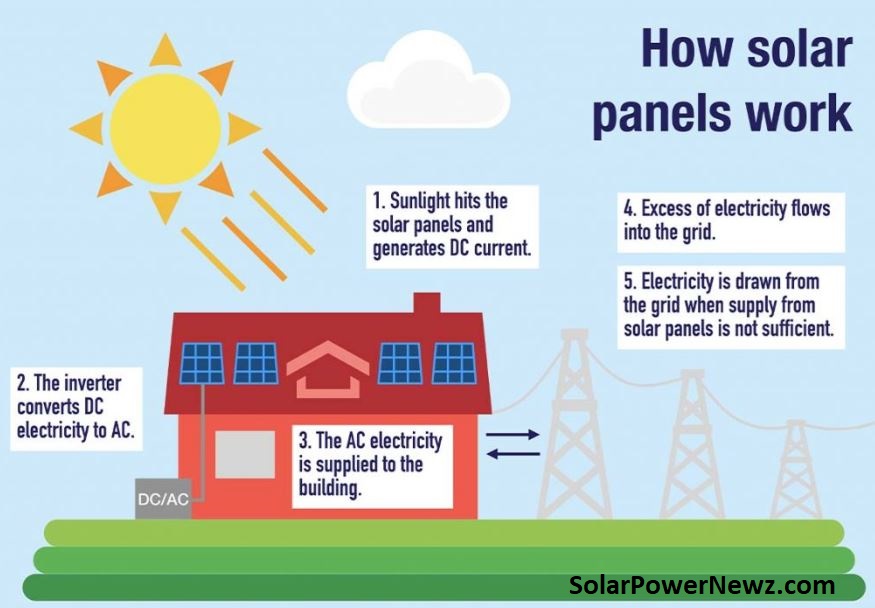
When the sun shines on a solar panel, the energy absorbed by the PV cells in the panel. This energy generates electrical charges that move in response to an internal electric field in the cell, causing electricity to flow.
Our sun functions as a natural nuclear reactor. It emits photons, which are tiny packets of energy that travel 93 million miles from the sun to Earth in about 8.5 minutes. Every hour, enough photons collide with our globe to generate enough solar energy to meet the world’s energy needs for a whole year.
Currently, solar power accounts for only 5% of total energy consumption in the United States. However, as solar technology advances and the cost of going solar falls dramatically, our ability to harness the sun’s abundant energy grows.
Solar became the world’s fastest-growing source of power in 2017, according to the International Energy Agency, marking the first time that solar energy’s growth had overtaken that of all other sources. Solar has grown and broken records all around the world since then.
How Does Weather Affect Solar Energy?
Even though it may not be how you’d expect, weather conditions can have an impact on how much electricity a solar system produces.
It goes without saying that a clear, sunny day is optimal for harnessing solar energy. Solar panels are, however, more effective in colder climates than in warmer climates, just like other electronics. It’s possible that the panel will produce more electricity in the same amount of time as a result. Lower voltage and less electricity are produced by the panel as the temperature rises.
Solar panels may be more effective in colder temperatures, but it does not mean that they always generate more electricity in the winter than in the summer. Summer months are warmer and tend to have more sunny days. The sun is typically visible for longer periods of the day in addition to having less clouds overhead. Despite the fact that solar panels are less effective in the heat, they will probably generate more electricity in the summer than in the winter.
Solar Technologies
Solar energy can be used in three ways: photovoltaics, solar heating and cooling, and solar energy concentration. Photovoltaics use an electronic technology to generate electricity directly from sunlight and can be used to power everything from small electronic equipment like calculators and traffic lights to homes and large commercial companies.
SHC and CSP applications both use solar heat to provide space or water heating in SHC systems or to power conventional power generation turbines in CSP power plants.
Types Of Solar Energy

Photovoltaic technology transforms sunlight directly into electricity. Its heat is captured using solar thermal technology. Both of these technologies use the Sun’s energy, both locally and in large-scale solar farms.
To harness it, two primary technologies have been developed:
- Photovoltaic solar technology turns sunlight directly into electricity using panels composed of semiconductor cells.
- Solar thermal technology collects the heat of the sun. This heat is either used immediately or transformed into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity, a process known as concentrated solar power. This heat is either consumed immediately (lowtemperature solar thermal) or turned into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity (concentrated solar power – CSP).
1. Photovoltaic Solar Power
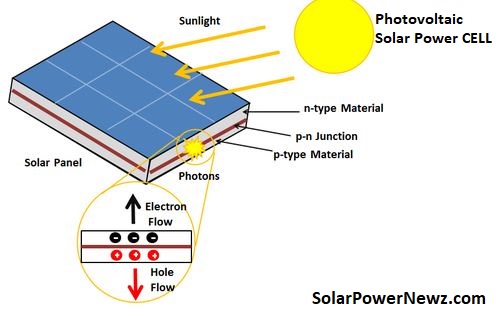
Light is converted into electricity through the photovoltaic effect (or photoelectric effect). Edmond Becquerel, a French physicist, discovered it in 1839, and it was first exploited in industrial applications in 1954. When electrons are displaced, an electric current is formed. Photons (light particles) are used to activate the outermost electrons of some semiconductor components.
In practise, a semiconductor, often silicon, converts light that strikes a photovoltaic cell into electricity. A photovoltaic module is made up of multiple cells that create direct current, which an inverter converts to alternating power. Panels can be utilised in both small and big systems.
2. Solar Thermal
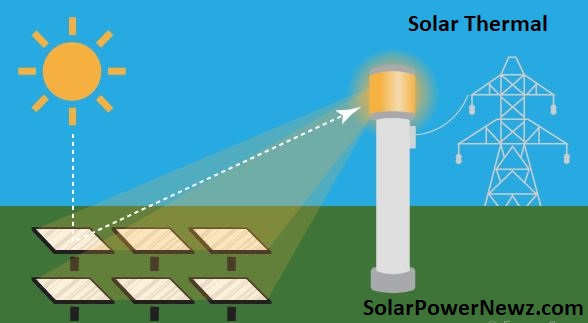
Solar thermal is a time-tested method that saves energy and reduces carbon emissions. A solar thermal system works by capturing and converting the sun’s energy into heat, which is then delivered into your house or business’s heating system as hot water or space heating.
In conjunction with a boiler, collector, or immersion heater, solar thermal panels are employed. To keep the water from freezing in the winter, the solar collector will use the sun’s rays to heat a transfer fluid, which is a mixture of water and glycol. The collected heat is transported to a heat exchanger inside a water cylinder. The exchanger’s heat will then heat the water inside the cylinder.
The water will flow back to the collectors for reheating when the liquid has released its heat. When there is enough heat available, a controller will ensure that the fluid circulates to the collector. Solar thermal technology has been demonstrated to be dependable and low-maintenance.
3. Concentrated Solar Power
The heat from the sun’s rays is concentrated by collectors in this second type of thermal solar energy technology in order to heat a transmission fluid (such as gas, oil, or molten salt) to a high temperature. The liquid warms a network of water, creating steam, which spins a turbine (using mechanical energy), creating electricity.
Huge power plants with curved or flat mirrors spread out over huge areas capture heat from the sun’s rays. The method works best in countries with lots of sunshine, such desert areas.
4. Utilising solar energy
The solar energy that the sun gives can be harnessed in a solar power plant to produce electricity that is widely used in commercial settings. We are all aware that most power plants require fossil fuels, which are not renewable, to heat water.
Steam produced when water boils drives a big turbine, which activates the generator and begins the process of producing power. Burning fossil fuels releases air pollutants and greenhouse gases, making it risky for the environment and people’s health as well as a bad way to generate power.
The good news is that a new generation of solar-powered power plants is being introduced.
These plants use the sun as a heat source in three different ways:
- The sun’s energy is captured by long rectangular, curved mirrors that point toward the sun in parabolic-trough systems. In this way, they aid in concentrating sunlight on an oil-filled pipe. To generate electricity, oil is cooked and used to boil water in a traditional steam generator.
- A dish/engine system makes use of a mirrored dish the size of a huge satellite dish to receive and focus the sun’s heat on a receiver. This receiver absorbs heat and delivers it to an engine’s fluid. Heat causes fluid to circulate against the piston or turbine, resulting in mechanical strength. This electricity is utilised to power a generator or alternator, which produces electricity.
- A power tower system focuses sunlight on the top of a tower, where a receiver containing molten salt resides, using a huge area of mirrors. Traditional steam generators employ salt heat to generate power. Because molten salt maintains heat well, it can be held for days before being transformed into electricity. This means that electricity can be generated even on cloudy days or after sunset.
5. Solar Water Heating System
Natural phenomena such as how shallow water in lakes or at the shallow end of beaches is frequently warmer than deep water served as the inspiration for the Solar water system. This is because, in shallow waters, sunlight can heat the lake or ocean floor, which subsequently heats the water.
The solar water heating system for homes, which consists of two components: a solar collector and a storage tank, was created as a result to mimic this.
A flat-plate collector mounted on the roof and facing the sun is the most frequent collector. Small tubes run through the box, carrying fluid to heat – either water or other liquids, such as an anti-freeze solution. The fluid travelling through the tubes heats up as the heat in the collector increases. The hot liquid is subsequently stored in the storage tank.
A similar method is frequently used to heat swimming pools.
6. Passive Solar Heating
Another way to harness solar energy is by passive solar heating and the daylight approach. This is not a novel idea; in fact, ancient civilizations such as the Anasazi Indians of Colorado pioneered passive solar architecture in their dwellings.
The influence of the sun is simple to understand: step outside on a hot sunny day and you can feel the sun. Buildings may “feel” the sun’s energy if they are well designed.
South-facing windows, for example, will receive more sunshine, while structures can also store heat and absorb solar materials, such as sun floors and walls.
These materials heat up during the day and gradually release heat at night when the heat is most needed. Other architectural elements, such as a greenhouse-style sunspace, concentrate too much heat that can be used to heat an entire building with proper ventilation.
Such characteristics increase not just the direct benefit of the sun’s heat, but also the sunshine itself. Even better, there are measures to ensure that these facilities do not overheat buildings, especially on hot days.
Advantages Of Solar Energy
Solar energy has significant advantages over traditional energy systems because it eliminates weaknesses in systems that were previously thought to be irreversible. Solar power for residential energy generation includes drawbacks, which are discussed in another article, but they are outweighed by the benefits stated below.
Solar energy has the following advantages:
- Raw materials are both renewable and limitless. The amount of available solar energy is mind-boggling, nearly 10,000 times what people now consume, and it is constantly replenished. If caught correctly, a modest 0.02% of incoming sunlight would be enough to replace every other fuel source currently in use.
- Solar energy is zero-emission. Solar panels emit no pollutants, yet their manufacture and construction have an impact on the environment.
- Solar energy is appropriate for isolated places that are not served by power grids.
- Solar energy creates green jobs. Solar panel manufacturing for home use is becoming an increasing source of employment in research, manufacturing, sales, and installation.
- Because solar panels have no moving parts, they make no noise. Wind turbines, by comparison, require noisy gearboxes and blades.
- Solar energy is cost-effective in the long run. Solar panels and installation have a high initial cost, however this is quickly compensated by energy bill savings. They may eventually generate a profit from their use.
- Solar energy utilises net metering, which is the practise of compensating homes for the electricity they generate and return to the power system.
- Solar energy may result in government tax breaks. Federal subsidies in the United States credit up to 30% of system expenses, while each state gives its own incentives. California, endowed with ample sunshine but beleaguered by high electric rates and an overburdened grid, was the first state to provide large renewable-energy incentives to individuals and businesses.
- Solar energy is dependable. Many households prefer solar energy because it is almost resistant to utility company failures, which might manifest as political or economic unrest, terrorism, natural disasters, or brownouts due to misuse. The 2003 Northeast Blackout disconnected 55 million people across two nations, although rolling blackouts are common in various South Asian countries and, on occasion, in California and Texas.
- Solar energy reduces international energy expenses. In many countries, a significant portion of earnings is spent to pay for imported oil used in power generating.
Disadvantages Of Solar Energy
While the numerous benefits of solar energy may lead some supporters to overlook the technology’s small drawbacks, these flaws must be acknowledged or resolutions will be stalled. We should be honest about the system’s shortcomings and work to improve solar energy systems into really ecologically friendly alternatives.
The following are the most common criticisms about solar energy:
- There is a lack of consistency and dependability. Solar systems rely on the consistent absorption of sunlight, namely subatomic particles known as photons, which are easily discouraged.
- Size. A big solar array is required to power an entire building. Unfortunately, photovoltaic technology is still in its infancy, therefore we must create vast arrays to compensate for the inefficiency of single panels for the time being. To turn the panels as they follow the sun across the sky, a large mechanical orientation system may be necessary. Batteries, too, can take up a lot of room.
- Deterioration of the panel. Solar panels, like anything else exposed to the sun, are eventually harmed by UV light. Rain, snow, filth, temperature swings, hail, and wind are all dangerous.
- Cost. The quantity of solar array panels required to capture energy for a whole home often costs tens of thousands of dollars, making the electricity produced far more expensive than that provided by traditional power sources.
- Pollutants in the environment. Among the more infamous chemicals found in panels and accompanying equipment are. Cadmium. Cadmium is safe when encased inside solar panels. Cadmium can cause substantial environmental damage if it leaks from the panel.
- Lead. Solar arrays require batteries, notably deep-cycle lead-acid batteries, to assure a consistent supply of electricity. They contain lead and sulfuric acid, both of which are extremely harmful to aquatic life.
- Considerations for the roof. Solar arrays are frequently built on building rooftops in order to take use of the huge, unoccupied, sunlit space. As a result, repairs to the underlying roof become more difficult and frequently necessitate the removal of the solar installation before even ordinary roof maintenance can be completed.
- Appearance. Solar arrays, whether you like it or not, make a statement, and neighbours and passersby will notice. Many homeowners are naturally hesitant to install a huge solar array on a tile roof that is otherwise appealing. This problem is being addressed by the development of photovoltaic shingles, windows, and other technologies that mix in with existing roof surfaces.
What Is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is defined as solar radiation that can generate heat, cause chemical processes, or generate electricity. The overall amount of solar energy received on Earth is far greater than the world’s current and projected energy needs.
What Is Solar Energy In Simple Words?
The solution is straightforward: solar energy. Solar energy is just light and heat emitted by the sun. People can use the sun’s energy in a variety of ways, including: Photovoltaic cells are solar cells that turn sunlight into electricity.
What Are 5 Advantages Of Solar Energy?
Advantages of Solar Energy:
Renewable Energy Source. The fact that solar energy is a completely renewable energy source is the most significant advantage of solar panels among all its other advantages.
Reduces Electricity Bills.
Diverse Applications.
Low Maintenance Costs.
How Does The Solar Energy Work?
Solar panels basically record the sun’s energy and then work to turn that energy into power for your home. When sunlight strikes solar panels, it is absorbed by photovoltaic cells and delivered to an inverter, where it is changed from direct current DC electricity to useful alternating current electricity.
What Are The 2 Main Disadvantages To Solar Energy?
The main drawbacks to solar energy are:
Reduced power output in cloudy weather.
Zero output at night.
Solar panels can’t store electricity.
Solar energy is direct current and needs converting for a.c. Appliances.
Solar panels are inefficient, 20% maximum.
How Do You Explain Solar Energy To A Child?
Solar power is energy that is created directly from sunshine. Solar energy can be used to generate heat or transformed into electricity. We do not consume any of the Earth’s resources, such as coal or oil, when we use solar electricity. As a result, solar power is a renewable energy source.