In this article we will discuss What is solar energy, and how is it converted into electricity. The earth intercepts a substantial quantity of solar electricity, 173 trillion terawatts to be exact, according to scientific research. That is around 10,000 times more power than the entire world population. This demonstrates that the sun is the most abundant source of energy on the globe and that it may one day be the most relied-upon source of energy.
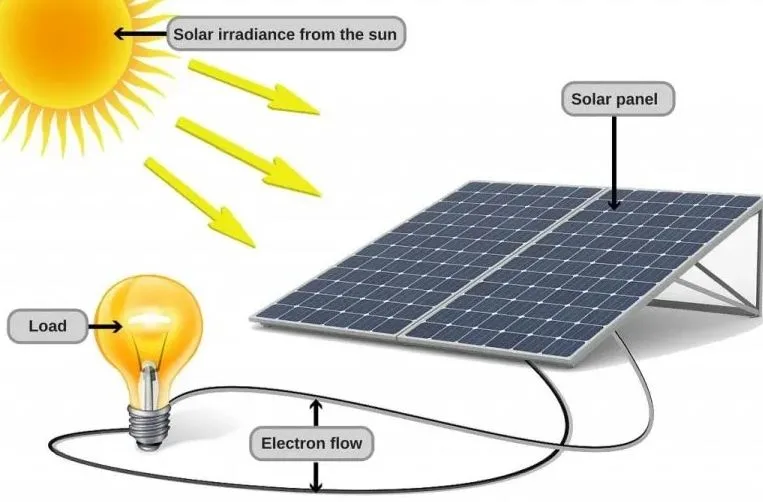
Table of Contents
Historically, fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas, and coal have met the world’s electrical demands. However, these energy sources have two major drawbacks:
They are more responsible for global warming and acid rain pollution, which have a severe influence on many creatures, plants, and humans in the ecosystem.
Few countries have complete access to fossil-fuel-based energy supplies, potentially leading to global political and economic instability.
Solar energy is the ideal solution because it is a renewable resource that will never run out. It delivers an infinite and consistent supply over time. Solar energy is also a green energy source because it produces no pollutants throughout the energy generation process.
What is solar energy, how is it converted into electricity
What is Solar Energy?

The energy produced by the sun in the form of heat and light is referred to as solar energy. It is one of the most renewable and easily accessible energy sources on the world. Because it is abundant and free, and does not belong to anyone, it is one of the most important non-conventional energy sources. People have exploited solar energy since ancient times by employing rudimentary magnifying glasses to concentrate the sun’s light into beams so hot that wood caught fire.
Generally, solar energy can be transformed into heat energy or electricity. Solar energy is derived from the sun. It is mostly applied in two ways:
1. Through the production of electricity
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) devices or solar cells are used in this technology to convert the sun’s energy into electricity. Photovoltaic gadgets generate energy directly from sunlight via an electrical process that occurs naturally in certain material types known as semiconductors.
Electrons released by solar rays are stimulated to go through an electronic circuit, supplying power to the grid or directly powering electrical equipment. This type of energy can power solar watches, calculators, and traffic lights. They are frequently utilised in areas that are not linked to the power grid.
2. Solar collector devices
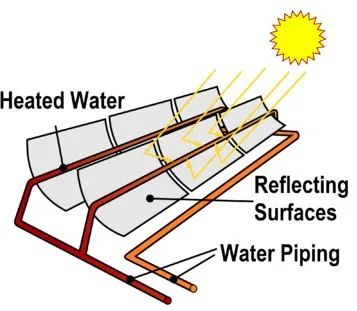
A solar thermal collector generates heat by absorbing sunlight. This method uses the sun’s energy to heat water (solar hot water panels) for use in home appliances such as water heaters, hot tubs, and ground pools. Concentrated solar power plants use more complicated collectors to generate energy by heating a liquid, which turns a turbine attached to a generator. Simple collectors are commonly used for space heating in commercial and residential buildings.
Solar energy produced into electricity can be used immediately to power lights or a variety of other devices. Even better, it can be stored in batteries for later use. Solar cells typically produce direct current (DC) electricity. It can, however, be turned into AC (alternating current) with an inverter. Solar energy produced into heat energy for water heating can be used immediately or stored as hot water in tanks for later use.
Solar energy can be classified as either active or passive depending on how it is captured and used. While mechanical equipment is not used in passive solar energy, special solar heating equipment is used in active solar energy to convert solar energy to heat energy. The employment of mechanical equipment such as photovoltaic cells, solar thermal collectors or pumps, and fans to trap solar energy is referred to as active solar.
Depending on how it is gathered and used, solar energy can be classed as either active or passive. While mechanical equipment is not used in passive solar energy, special solar heating equipment is used in active solar energy to convert solar energy to heat energy. Active solar is the use of mechanical equipment to trap solar energy, such as photovoltaic cells, solar thermal collectors or pumps, and fans.
How Solar Energy is Converted to Electricity?
Installing photovoltaic (PV) or solar cells is the first stage in converting solar energy to electricity. Photovoltaic refers to the combination of light and electricity. These cells absorb solar energy and convert it to electricity. These solar cells are comprised of photovoltaic materials, which means that when the sun’s rays reach the Photovoltaic cell, the photons of light startle the electrons inside the cell, causing them to start flowing and, eventually, producing energy.
It would be advantageous to be aware of the market possibilities while searching to purchase solar panels. Here’s a rundown of the important ones:
- Polycrystalline – This utilizes Multicrystalline Silicon
- Monocrystalline – This is perfect for compact places.
- Thin Film – Usually larger in size and much more efficient during the day.
The difference between monocrystalline and polycrystalline materials is due to the composition of the silicon substrate used to create solar cells and, ultimately, solar panels. Polycrystalline denotes several crystals, whereas monocrystalline denotes a single crystal. The greater the crystal size, the more efficient the solar cells, which is why monocrystalline cells are often 10 – 15% more efficient than polycrystalline crystals.
How Solar Panels Work?

The solar panel should be installed in an open location that is not obscured by trees or other structures. A roof is usually the best option. The inverter is then used to connect it to the building. An inverter is a device that transforms alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) (direct current). In this scenario, the alternating current represents the energy produced by the solar panels. This solar energy is turned into alternating current (AC). The objective for converting direct current to alternating current is to allow the energy to be utilised by various home appliances in the same manner that regular electricity powers your devices.
Considerations to Keep in Mind Before Installing Solar Panels
Before you take any steps to put a solar panel in your home, make sure that solar power is appropriate for you and your home. Then, check that there is enough sunlight in your area. The appropriateness of solar energy varies greatly depending on how much sunlight a location receives. If your neighbourhood does not receive enough sunlight, installing solar panels is not the greatest option.
After ensuring that your area receives enough sunlight, ensure that appropriate installation space is accessible. We’ve discovered that solar panels are almost often installed on building roofs. While this is admirable, it is not the only choice. If you have an open space in your backyard, it would be excellent for ground mounting. The backyard alternative is suitable for individuals whose roofs are substantially shaded or who do not require solar panels architecturally. It is also critical to understand the local rules related solar panel installation in order to avoid getting into trouble with the local authorities. This information is available from your local solar energy professional.
Environmental Impact
Despite the fact that solar energy is one of the cleanest and most sustainable energy sources available today, it has certain environmental effects. Solar energy is generated using photovoltaic cells. However, the manufacturing of solar cells to create that energy consumes silicon and produces some waste. Inadequate management of these materials can endanger both people and the environment. Solar generating installations may demand a large plot of land, potentially affecting existing ecosystems. Solar energy does not pollute the environment when converted to electricity via solar panels. It is abundant and does not contribute to global warming.
Future of Solar Energy
Before delving into a discussion on the future of solar energy, three facts must be considered:
Humans and other living forms on Earth are seriously threatened by climate change, which is a true phenomena.
We must lead the charge in decreasing greenhouse gas emissions by 80% by the year 2050 if we are serious about lowering the risk that our children will suffer the worst effects of climate change. Energy use is responsible for 60% of world emissions, thus we must immediately start adopting low-carbon solutions broadly.
Solar Energy is the largest energy resource, by far
In addition to geothermal, nuclear, and tidal energy, sunlight is another form of sustainable energy. Fossil fuels are simply solar energy that has been kept in storage for many years (using animal and plant remnants as batteries). Wave and wind power were first fueled by solar energy. To fulfil the world’s rising energy demand, terawatt (TW)-level deployment is only possible with wind, solar, and perhaps nuclear power.
There is significant scale-up of solar photovoltaic technologies.
Compared to other energy technologies, photovoltaic technology is expanding more quickly. All installed solar systems’ capacity has tripled every two years since 2000, reaching 200 gigatonnes-peak (GWp) in 2014. This exponential growth is still accelerating. Within a decade, solar energy will likely meet all of the world’s energy needs if photovoltaic technology development continues at its current pace.
However, given that major economies like the United States and China are spending billions of dollars on the development and use of solar energy technologies, the future of solar energy appears promising. Furthermore, most countries seeking to lessen their dependency on fossil fuels find solar energy to be desirable because it is a renewable resource.