What Is Wind Energy?

In this article, we will discuss What Is Wind Energy, Pros, And Cons. Wind power or wind energy refers to the practise of harnessing the wind to generate mechanical power or electricity. Wind turbines transform wind kinetic energy into mechanical power. This mechanical power can be employed for specialised tasks (such as grain grinding or water pumping) or transformed into energy by a generator.
Wind energy is a popular sustainable, renewable energy source with a lower environmental impact than burning fossil fuels.
Wind is an intermittent energy source that cannot be dispatched when needed. Locally, there is variable performance that is steady year after year but varies considerably across shorter time periods. As a result, it must be used in tandem with other power sources to maintain a consistent supply.
What Is Wind Energy, Pros, And Cons
Table of Contents
Wind Energy Basics
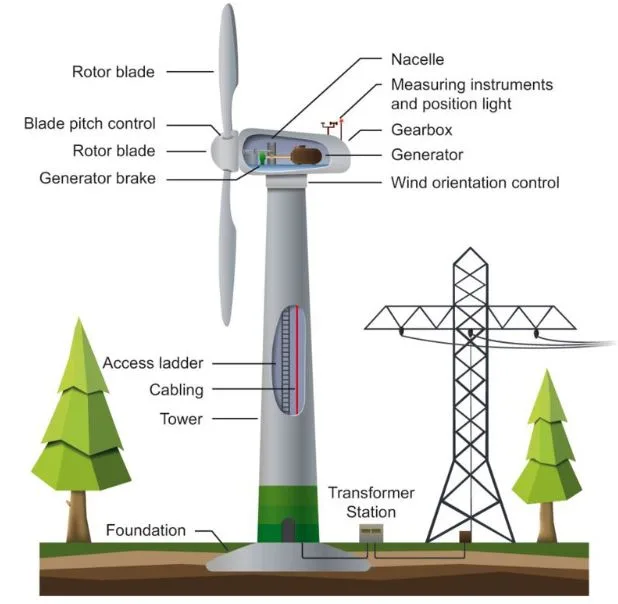
The wind is created by the sun’s uneven heating of the atmosphere, changes in the planet’s surface, and the rotation of the earth. Wind flow patterns are influenced by mountains, bodies of water, and vegetation.
Wind turbines use propeller-like blades that rotate around a rotor to convert wind energy into electricity. The rotor rotates the driveshaft, which in turn rotates an electric generator.
Three major elements influence how much energy a turbine can extract from the wind:
- Wind speed,
- Air density, and
- Swept area.
The Equation For Wind Power

Wind Speed
The amount of energy in the wind varies with the wind speed cube. In other words, as the wind speed doubles, the energy in the wind increases by eightfold (23 =2x2x2=8). Small changes in wind speed have a significant impact on the available wind power.
Density Of The Air
The more energy the turbine receives, the denser the air. The density of the air changes with altitude and temperature. At higher altitudes, air is less thick than at sea level, and warm air is less dense than cold air. If all other factors remain constant, turbines will produce more electricity at lower altitudes and in areas with cooler average temperatures.
Swept Area Of The Turbine
The larger the swept area (the region through which the rotor spins), the more wind power the turbine can capture. Because the swept area is A = pir2, where r is the radius of the rotor, a small increase in blade length results in a bigger increase in turbine output.
Things You Didn’t Know About Wind Power
- Wind power has been employed by human civilizations for thousands of years. The wind was employed to crush grain or pump water in the early kinds of windmills. Wind is now used to create electricity by contemporary wind turbines. Discover how a wind turbine works.
- Wind turbines of today are far more complex equipment than the original grassland windmill. A wind turbine can have up to 8,000 distinct parts.
- Wind turbines are massive. Wind turbine blades are often over 190 feet long, and turbine towers are typically 295 feet tall – roughly the height of the Statue of Liberty.
- Wind turbines become taller as wind speeds increase, allowing them to reach higher altitudes above the ground, where it is even windier. Wind Resource Maps from the Department of Energy will help you identify average wind speeds in your state or hometown. A paper from the Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory provides more information about taller wind turbine prospects.
- The majority of wind turbine components installed in the United States are manufactured in the country. There are around 500 wind-related industrial sites spread across 43 states, and the US wind industry employs over 114,000 people.
- Offshore wind represents a significant possibility to deliver power to densely populated coastal communities, and the country’s first offshore wind farm was built off the coast of Rhode Island in 2016. Examine what the Energy Department is doing to promote offshore wind development in the United States.
- Utility-scale wind power is already installed in 41 states, with North Carolina’s first utility-scale wind farm coming online in early 2017. All 50 states, as well as Puerto Rico, Guam, and the US Virgin Islands, have distributed wind installed.
- Wind power capacity in the United States was 105.591 megawatts by the end of 2019, making it the largest renewable energy source in the country. That’s enough electricity to power 29.5 million average American households for a year.
- Wind energy is inexpensive. Wind pricing for recent power contracts and levelized wind prices (the price a utility pays to buy power from a wind farm) are 2-4 cents per kilowatt-hour.
- Wind energy accounts for more than 10% of total electricity generation in 14 states, including Kansas, Iowa, and Oklahoma, where it accounts for more than 30%.
Advantages Of Wind Energy
Wind energy provides advantages and is an efficient option for many different places of the world because it does not rely on direct sunshine exposure like solar energy.
1. Wind Energy Is Clean And Renewable

In contrast to coal, natural gas, or oil, wind energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions. While there are some environmental concerns associated with the construction of big wind farms, wind turbines themselves do not require the use of any fossil fuels once operating.
Wind energy is also entirely renewable and will never run out. In contrast to traditional fossil fuel supplies, which renew very slowly, wind occurs naturally in our atmosphere, therefore we do not need to be concerned about future supply difficulties.
2. Free Fuel
There is no need for fuel because wind turbines run solely on wind-generated power. The turbine does not need to be fueled or connected to power after it is completed and mounted.
This also lowers the overall cost of maintaining large-scale wind farms in compared to other kinds of renewable energy, which may necessitate some energy expenditure.
3. Wind Energy Has Low Operating Costs
Wind farms or individual turbines can be costly to install in terms of upfront costs. However, once operational, operating costs are quite minimal; their fuel (wind) is free, and the turbines don’t require much maintenance over their lifetime.
4. Wind Energy Is Space-Efficient

Wind farms can take up a lot of land space when combined; yet, the actual turbines and equipment take up very little room. As a result, land utilised for wind turbines is frequently also used for other reasons, such as farming.
5. Advances In Technology
The most recent technological advancements have transformed basic wind turbine ideas into incredibly efficient energy harvesters. Turbines are available in a variety of sizes, opening up the market to a variety of businesses and individuals for usage at home on larger lots and plots of land.
As technology advances, so do the structure’s capabilities, resulting in designs that generate more electricity, require less maintenance, and run more quietly and safely.
Disadvantages Of Wind Energy
Although wind energy is a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy source, it does have drawbacks and restrictions.
1. Wind Energy Is Intermittent
Because the effectiveness of a wind turbine in generating power is dependent on the weather, it can be difficult to forecast how much electricity a wind turbine will generate over time. The turbine’s rotor will not spin if wind speeds are too low on any given day.
This means that wind energy isn’t always available for dispatch during peak periods of electricity demand. Wind turbines must be combined with some form of energy storage technology in order to be used entirely.
2. Wind Energy Causes Noise And Visual Pollution
One of the most significant disadvantages of wind energy is noise and visual pollution. Wind turbines can be noisy when in operation due to both mechanical operation and the wind vortex formed as the blades rotate.
Furthermore, because wind turbines must be constructed high enough to capture a significant quantity of wind, they frequently disrupt otherwise picturesque scenery such as mountain ranges, lakes, and coastlines.
3. Wind Plants Can Impact Local Wildlife
The blades of a wind turbine are very big and rotate at tremendous speeds. Unfortunately, their blades can damage and kill flying creatures such as birds and bats. Wind farm building can potentially damage the natural habitats of local wildlife if not done in a sustainable manner.
However, technical developments and appropriately sited wind farms can help to alleviate some of these issues.
4. Looks
Wind turbines must be built high in order to capture enough wind, making them a noticeable feature of any landscape. Some individuals regard enormous wind turbines to be an eyesore, however this is a matter of personal preference.
5. Location Limitations
Wind turbines must be erected in an area where they will produce enough electricity to be economically viable. Wind farms are most suited for coastal areas, hilltops, and open planes – in short, anyplace there is a strong, consistent wind.
The majority of appropriate locations are located in remote areas far from cities and towns, in more rural areas, or offshore. As a result of the distance, new infrastructure, including as power lines, must be constructed in order to link a wind farm to the electricity grid.