What Is Windmill, Types, And Uses
Windmills are one of the essential pieces of technology that enabled our forefathers to convert the strength of the wind into a physical force that can be utilised for a wide range of purposes, from most conventional activities like grinding grains and transporting water to many more industrial and agricultural requirements.
This page will explain what a windmill is, the history of windmills and how they evolved into modern forms, and how they work.
What Is Windmill?

A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy via vanes known as sails or blades, mostly to mill grain (gristmills), although the term is also applied to wind pumps, wind turbines, and other applications. Such machines are commonly referred to as wind engines.
A windmill is a device that uses sails set on a revolving shaft to harness wind energy. The sails are mounted at an angle or with a minor twist, so that the force of the wind against them is divided into two components, one of which imparts rotation in the plane of the sails.
Windmills, like waterwheels, were among the first prime movers that supplanted humans as a source of power.
Windmills were employed throughout the high mediaeval and early modern periods; the horizontal or panemone windmill first arose in Greater Iran in the 9th century, and the vertical windmill first appeared in northwestern Europe in the 12th century. There are roughly 1,000 windmills in the Netherlands today, and they are regarded as an emblem of Dutch culture.
Table of Contents
Windmill History
Modern windmills as we know them now initially appeared in the Middle East and Western Asia in the 8th and 9th century. Wind turbines were first manufactured in 1887, and after the 1900s, an increasing number of wind pump windmills got the ability to generate electricity as a supplementary task.
Wind energy was used to drive boats along the Nile River as early as 5,000 BC. Windmills with woven-reed blades were grinding grain in Persia and the Middle East by 200 BC, and primitive wind-powered water pumps were utilised in China.
Wind energy innovations eventually spread over the world. Wind pumps and windmills were widely used for food production in the Middle East by the 11th century. Wind technology was introduced to Europe by merchants and Crusaders. The Dutch invented huge windpumps to drain the Rhine River Delta’s lakes and marshes. Wind energy technology was finally brought to the Western Hemisphere by European immigrants.
Windmills were used by American colonists to grind grain, pump water, and cut wood at sawmills. Thousands of windpumps were installed by homesteaders and ranchers when they inhabited the western United States. Small wind-electric generators (wind turbines) were also commonly utilised in the late 1800s and early 1900s.
As rural electrification projects in the 1930s stretched electricity connections to most farms and ranches across the country, the number of wind pumps and wind turbines decreased. However, several ranches continue to use wind turbines to deliver water to their livestock. Small wind turbines are regaining popularity, mostly to provide electricity in isolated and rural regions.
Types Of Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are classified into two types based on their axis of rotation: horizontal-axis turbines and vertical-axis turbines.
1. Vertical-Axis Turbines
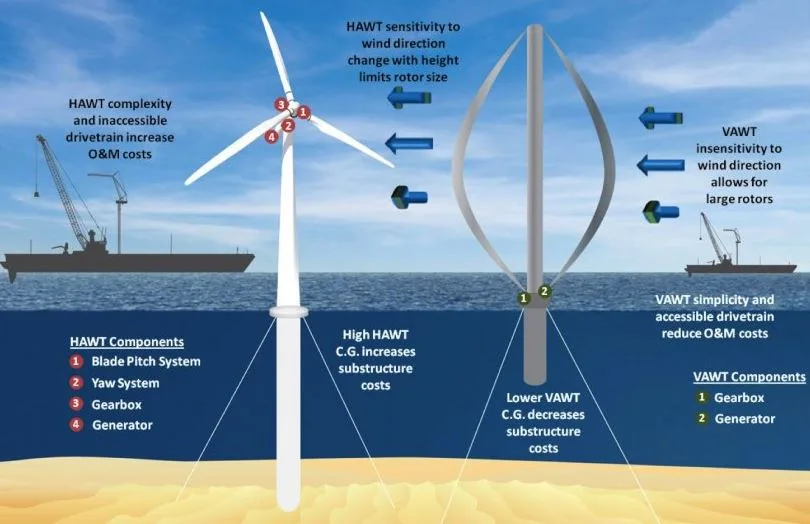
Vertical axis windmills were quite popular and widely used during the early stages of development. It is designed in such a way that the blades are perpendicular to the ground. Because of their ineptitude, these vertical axis windmills were eventually replaced by horizontal axis windmills. It was mostly used to crush grains or pump water.
2. Horizontal-Axis Turbines
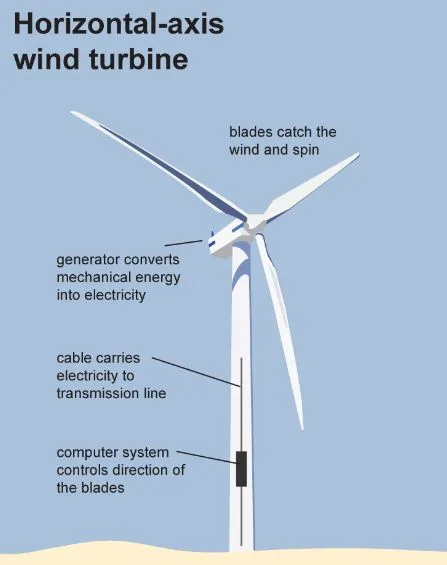

Because of their efficiency and production, horizontal axis windmills have garnered many fans. It is noted for its elasticity design since it captures more wind and allows the operator to easily adjust the direction according on the wind flow.
Check read our page on what a wind turbine is and how it works for additional information.
Types Of Windmills

Windmills are classified into four types:
- Post mill.
- Smock mill.
- Tower mill.
- Fan mill.
1. Post Mill
The post mill is a type of windmill that is supported by a post that pivots to capture the wind. It is the oldest type of windmill in Europe. Its distinguishing characteristic is that the entire mill body that houses the machinery is situated on a single vertical post that can be moved to bring the sails towards the wind.
Post mills dominated the European scene until the nineteenth century, when tower mills began to replace them.
Types Of Post Mill
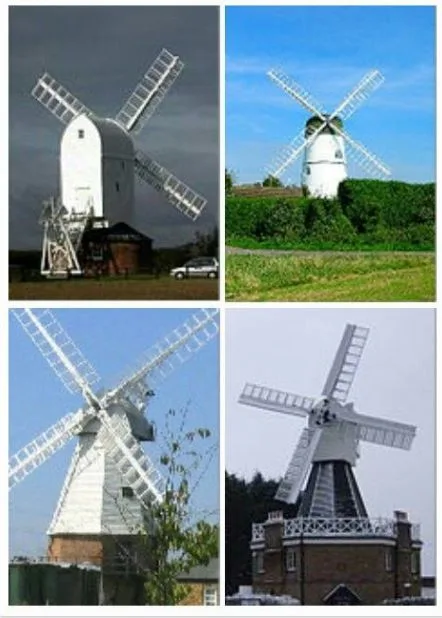

There are various kinds of post mills.
- Sunk post mill
- Open trestle post mill
- Post mill with roundhouse
- Hollow post mill
- Composite post mill
- Paltrok post mill
2. Smock Mill
The smock mill is a form of windmill with six or eight sides that is slanted, horizontally worn, thatched, or flaking. It is topped with a rotating roof or cap that directs the sails into the wind.
The smock mill is typically composed of wood and sits on a brick foundation. It varies from a post mill in that, unlike a tower mill, the body does not rotate; instead, the cap rotates to face the wind.
3. Tower Mill
A tower mill is a form of vertical windmill that consists of a brick or stone tower with a wooden “cap” or roof that rotates to allow the sails to face the wind.
Tower Mill is a cotton mill in the English town of Dukinfield, Greater Manchester. It is a historic structure.
It was designed in 1885 by Potts, Pickup & Dixon and spun cotton using mules and spinning frames until 1955, when it was employed by numerous industries and broken down into small parts according to one-point plans.
It was even decided to turn the mill into luxury apartments, however due to the 2007/08 crisis, this proposal was scrapped.
4. Fan Mill
Fan mills are typically single-use tiny windmill designs. It is mostly used to pump water and contains four to twenty blades.
Uses Of Windmill
- Windmills are mechanical devices that transform wind energy into electrical energy using wind turbines.
- Windmills have been used to pump groundwater and grind grain.
- The extraction of oil from seeds.
- Grains are milled.
- Tobacco, cocoa, dyes, spices, paints, and stock-watering are examples of goods processed.
Facts About Windmill
Windmills include several fascinating facts. We hope you find them enjoyable.
- Windmills were originally used to generate electricity in Persia and China in 200 BC.
- For hundreds of years, wind energy was employed to pump water and crush grain.
- In the 1940s, Vermont created the first modern turbine.
- Turbine towers are typically above 328 feet tall.
- Windmills provide 20% of the energy utilised in Portugal and Denmark.
- China has the most number of wind turbines.
- Every second Saturday in May, Holland observes ‘National Mills Day.’
- One megawatt of wind power can save around 2600 tonnes of carbon dioxide produced by fossil fuel-powered energy sources. The first windmill was built in the Netherlands in the ninth century.